Why are separate codes created for different countries? What is the code for our country - Russia? Telephone and postal networks are huge. Their entire size is quite difficult to imagine. They work around the clock, without breaks, as everyone needs urgent calls and letters received on time. So that people could call, for example, to another country, special codes were invented for each of them. A separate service unit is responsible for calls to a specific country, city, or region. Each one maintains its own code. Such calls will be charged more than calls within your own country or city. The code is also a method of protection and identification. All information about them is not hidden, anyone can use it.
What does the international number format affect?
Previously, mobile phones were used only for voice communication with other people, but now a phone number is required even when registering on a website, messenger or social network. On international portals, developers ask you to indicate the phone number in international format, that is, also enter the country code. If you ignore the requirement, the system will not register the user. Therefore, to speed up the registration process, people remember the correct format.
Each country has a standard that is used for mobile and landline numbers. However, sometimes there are national regulations beyond this that must be followed.
On the territory of Russia, the number eight is first prescribed in the number; this is one of the national rules that everyone follows. The first digit displays subscribers in the long-distance format. In Europe, the same principle is used to use zero, after which comes the main set of numbers.
Regardless of the country in which the subscriber is located and national characteristics, it will be possible to reach another user if you adhere to the international format. To contact a foreigner, the number starts with a plus. It will appear on the screen if you hold down the zero key.
After this, write down the country code, which consists of several numbers (no more than 3). In Russia it is 7, Australia - 61, Brazil - 55. It is worth checking the information in advance with the operator or via the Internet, since it is simply impossible to remember the codes for all countries. After specifying the country code, the region or operator number is dialed, only after that the subscriber’s digits are entered.
If you look at the cell numbers of Russian citizens internationally, they all consist of 3 digits, starting with 9. When the number starts with something else, it is considered corporate or home.
The region code consists of 3–5 digits, in Moscow even several options are used - 495 and 499. In Yekaterinburg, 343 is pre-dial, and in Murmansk - 8152.
The subscriber set also depends on the dialing in the region code, since the total number consists of 10 digits. In this regard, residents of Murmansk receive only 6 digits, and Yekaterinburg and Moscow - 7 each.
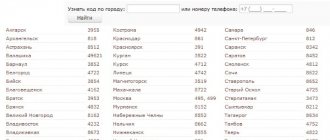
Beeline codes by Russian regions (table)
Each region of Russia can have several code values. In addition, the same prefix is found on phones from different mobile operators. This is due to the transfer of subscribers to another network while maintaining the number.
The table below shows Beeline digital codes.
| Regions | Codes |
| Khabarovsk Territory, Chukotka | 900 |
| Saratov region, Primorye | 902 |
| The entire territory of the Russian Federation, with the exception of: Kamchatka, Primorye, Chukotka, Sakhalin, Transbaikalia; Arkhangelsk, Amur, Vologda, Irkutsk, Kaliningrad, Kurgan, Kirov, Murmansk, Magadan, Novgorod, Pskov, Tambov, Tyumen regions (region); Jewish Autonomous Region (AO); Nenets, Khanty-Mansiysk, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug (AO); Penza, Khabarovsk territories; Karelia, Kalmykia, Komi, Buryatia, Tyva, Yakutia, Udmurtia, Chechnya | 903 |
| Ivanovo region, Chechnya, Primorye | 904 |
| The entire territory of Russia, with the exception of: Kamchatka, Primorye; Amur, Magadan, Sakhalin regions; Jewish Autonomous Region; Buryatia, Khakassia, Chechnya, Chuvashia, Dagestan, Altai | 905 |
| The whole country except: some northern regions (Transbaikalia, Primorye; Jewish Autonomous Okrug; Irkutsk region; Khabarovsk Territory; Kamchatka, Sakhalin, Yakutia, Buryatia); Magadan, Ryazan region; Chechnya, Chukotka | 906 |
| Primorye, Saratov region | 908 |
| The entire territory of the Russian Federation, with the exception of: certain northern regions (Transbaikalia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Primorye, Buryatia, Sakhalin, Yakutia, Chukotka); Irkutsk, Ryazan regions; Jewish Autonomous Region; Ingushetia, Chechnya | 909 |
| Everywhere except: Moscow, Tyumen (including Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug), Amur, Irkutsk, Sakhalin, Magadan regions; Jewish Autonomous Region; some northern regions (Transbaikalia, Primorye, Kamchatka, Chukotka; Perm and Khabarovsk territories; Buryatia, Komi, Yakutia); central zone (Kurgan, Kaliningrad, Kirov, Orenburg, Sverdlovsk, Chelyabinsk regions; Stavropol Territory; Udmurtia) | 960 |
| The entire territory of the country, with the exception of: northern regions (Nenets, Khanty-Mansiysk districts; Arkhangelsk, Irkutsk, Magadan, Murmansk, Sakhalin regions; Jewish Autonomous Okrug; Primorye, Transbaikalia; Krasnoyarsk Territory; Buryatia, Karelia, Chukotka); middle zone (Vologda, Kaliningrad, Novgorod, Pskov, Moscow, Ulyanovsk regions, Tatarstan, Udmurtia); southern Russia (Karachay-Cherkessia, Ingushetia, Kabardino-Balkaria, Chechnya) | 961 |
| The entire territory of the Russian Federation, with the exception of: regions of the Far North (Chukotka, Transbaikalia, Perm Territory; Irkutsk, Magadan, Murmansk, Tyumen regions, including the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug; Jewish Autonomous Okrug); central zone (Novgorod, Omsk, Kurgan, Orenburg, Pskov regions); southern Russia (Rostov region, Karachay-Cherkessia, Buryatia, Karelia, Komi, Udmurtia) | 962 |
| The entire territory of the country, with the exception of: northern regions (Transbaikalia, Irkutsk, Magadan regions; Jewish Autonomous Okrug; Buryatia, Yakutia; Nenets Autonomous Okrug); middle zone (Astrakhan, Vladimir, Orel, Kursk, Belgorod, Kemerovo, Voronezh, Kaluga, Ryazan, Lipetsk, Omsk, Smolensk, Orenburg, Yaroslavl region, Chuvashia); southern part of the country (Volgograd, Rostov regions, Adygea, Kalmykia) | 963 |
| The entire territory of the country, except: northern regions (Kamchatka, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Amur Region, Krasnoyarsk Territory); middle zone (Belgorod, Orenburg, Lipetsk, Voronezh, Bryansk, Kemerovo, Oryol, Kaliningrad, Tula, Kursk, Kurgan, Omsk, Tver regions); southern part (Volgograd, Rostov regions; Stavropol, Adygea, Altai, Kalmykia, Alania, Tatarstan, Tyva, Khakassia, Chuvashia) | 96 |
| North of the Russian Federation: Krasnoyarsk, Perm, Khabarovsk territories; Nenets, Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug; Amur, Murmansk, Arkhangelsk, Novosibirsk, Moscow, Leningrad regions; Karelia, Komi, Yakutia. Middle zone: Vologda, Kaluga, Kurgan, Novgorod, Omsk, Orenburg, Penza, Pskov, Ryazan, Saratov, Sverdlovsk, Tambov, Tver, Ulyanovsk, Chelyabinsk, Yaroslavl regions; Tatarstan, Udmurtia, Chuvashia. South of Russia: Krasnodar region; Astrakhan regions; Dagestan, Kabardino-Balkaria, Chechnya, Bashkortostan. | 965 |
| North of the Russian Federation: Primorye, Tyumen region, Krasnoyarsk region. Middle zone: Penza, Samara, Saratov, Moscow, Leningrad, Sverdlovsk regions; Tatarstan, Chuvashia. South of Russia: Chechnya, Alania, Dagestan; Volgograd region | 966 |
| The entire territory of the country, with the exception of: northern regions (Kamchatka, Chukotka, Transbaikalia; Amur, Magadan, Irkutsk, Sakhalin regions; Jewish Autonomous Okrug; Karelia, Komi; Nenets Autonomous Okrug; Khabarovsk Territory); middle zone (Vologda, Kemerovo, Belgorod, Vladimir, Ivanovo, Oryol, Tomsk, Voronezh, Kursk, Novgorod, Pskov, Kurgan, Lipetsk, Omsk, Tambov regions; Altai, Mordovia, Tyva); southern part of the country (Volgograd, Rostov regions; Stavropol region; Karachay-Cherkessia, Adygea, Alania, Kalmykia) | 967С |
| Northern regions: Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug; Primorye, Transbaikalia, Chukotka; Amur, Novosibirsk region; Jewish Autonomous Region; Khabarovsk region; Yakutia, Buryatia. Middle zone: Omsk, Chelyabinsk, Moscow, Leningrad regions. South of the country: Stavropol region; Volgograd region; Krasnodar region; Alania, Chechnya. | 968 |
| North of the Russian Federation: Krasnoyarsk and Khabarovsk territories; Transbaikalia; Amur, Irkutsk, Novosibirsk, Magadan, Tyumen regions, incl. Khanty-Mansiysk, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. Middle zone: Chuvashia, Tatarstan, Mari El; Bryansk, Belgorod, Kirov, Kostroma, Nizhny Novgorod, Penza, Saratov, Yaroslavl, Orenburg, Moscow, Leningrad regions; South of Russia: Karachay-Cherkessia; Volgograd region; Bashkortostan, Ingushetia, Dagestan, Kabardino-Balkaria, Alania, Chechnya | 969 |
How to indicate a number in international format?
If a person from another country calls a resident of the Russian Federation, then the international code of Russia must be indicated. Therefore, dialing begins with a plus, then the country code (7) is entered.
If a user registers on a website or in a messenger, then it is worth checking whether the form has a pre-set icon. The developers make it translucent so that a person understands in what format the number must be entered.
After +7 comes the area code or specific operator, and then the main number. Next, eleven digits are dialed if the international code of Russia is used. Using the same principle, numbers of subscribers from other countries are entered.
Order methods
In order to order or activate a service, you must use one of the following methods:
- combination of numbers. It is a unique combination of numbers, after which the user can connect to the selected service. This is convenient because the operation is quite quick and straightforward;
- number. This includes connecting to a tariff using the current phone number 222. A person can learn more about the services and choose the best offer;
- application. This means changing or connecting a tariff in the official Kyivstar application. In order to do this, you need to download it, log in to your account and select a service package.
What is a prefix?
A prefix is the operator code that comes immediately after 8 or +7. It is also used by subscribers to identify the operator in order to understand how expedient it is to call back a missed call and how much it will cost. Communication within the network occurs on preferential terms, so it is useful to clarify this information in advance.
The operator is found by three numbers; there are applications, websites for this, and some offer instant USSD commands to use the service for free. On thematic portals, the full number of the caller is entered, after which information about the region and operator is displayed. If you don’t want to waste traffic on this, you can download the Excel database, which indicates foreign and Russian formats.
When you need to find out the prefix for a call, the information is clarified with the operator or also searched on the Internet. Websites do not always provide reliable data, so it is safer to call the hotline.
How to save numbers?
Subscribers often leave contacts in the phone book using the number eight. At the same time, employees of communication stores insist that the Russian telephone code be used in international format. It’s faster to write one number, especially since the plus appears only when you press zero for a long time, but in this case there is a risk of communication problems.
An emergency business trip or an unexpected last-minute trip for which the user did not have time to prepare will not cause problems. When roaming, the SIM card is registered in another network, so to make a call or send an SMS you will need the Russian telephone code in international format. The same factor is taken into account when sending a contact to another person.
Price
Depending on different tariffs, the cost of calls abroad will vary. In order to choose the most profitable option, you should compare all possible tariffs for international calls. It is worth remembering that the price of the service depends on which tariff a particular state belongs to. Russia is included in the first tariff zone and communication has the following cost:
- the world is connected. It is a service in which one minute of conversation costs from 40 kopecks per minute. Thus, it is necessary to approximately understand the number and duration of all conversations per month;
- premium international calls. This means a service in which the number of your interlocutor will be displayed correctly, and the quality of communication will be at a high level;
- world connected basic. This package allows you to buy 20 minutes of conversation, the cost of which is 1 hryvnia per minute;
- SMS abroad. In addition to calls, each person can send messages to another country. To do this, you need to look at the features of the service and choose the most profitable option.
The emergence of this format
For convenience, a single unified system has been created, thanks to which users communicate with each other and the number is identified. The latter service is built into all tariffs and is provided free of charge.
There are two accepted numbering methods in the world: open and closed. The first of them allows you to call other subscribers without using an area code. A closed plan implies the introduction of a full-length number even for local calls; intercity communication or with foreigners follows the same scheme.
The open plan is more convenient, but it is rarely used, since everyone is trying to focus on the international format. Recently, Moscow completely switched to it, so numbers of 5 or 7 characters are no longer available to residents of the capital. This format remains only for communication within one region between landline phones. When traveling long distance you will have to indicate the number of the locality, and when communicating with foreigners you will have to additionally enter +7.