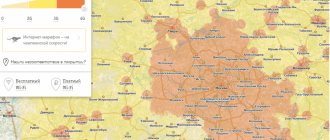
The mobile operator Tele2 is developing rapidly and is steadily expanding its coverage area and communication quality. Tele2 cell towers on the map below allow you to verify this; their number is sufficient to provide stable coverage to most regions of our country.
- Tele2 base stations operate on equipment from Nokia Networks and Flexi Multiradio
- The company is currently working towards the development of the 4G communication format
- Stations are located everywhere: rooftops, roadsides, subways and other places
Equipment
Our inquisitive readers are probably interested in knowing which towers Tele2 operates on? The telecommunications equipment that this cellular operator uses is truly first-class. Nokia Networks and Flexi Multiradio are the towers Tele2 uses, and these manufacturers produce the latest generation equipment.
Now this mobile operator aims to provide its customers with an uninterrupted signal in 4G format and is successfully working in this direction - residents of large cities have already seen this. In Moscow, St. Petersburg and many other cities, there is an LTE signal even in the metro. To verify this, we recommend reading the article about the Tele2 coverage map in the metro, which is available on our website.
Tele2 3g and 4g coverage map
The Tele2 coverage map is presented on the company's official website.
You should not use third-party sources on the Internet to obtain up-to-date information, since the data posted on them may differ significantly.
For the most remote regions, LTE450 is introduced, which is high-speed and requires the use of SkyLink equipment. If you do not have access to the network, then you can find out the latest information indicating cities in Russia about 3G and 4G connections by calling the support service by calling 611. An experienced employee of the company will answer any informational or technical question and help solve any problem.
How they work
How does a standard base station work? In a nutshell, your SIM card receives the signal issued by the nearest tower, thereby providing you with various communication services - the ability to make calls, receive and send SMS messages, and mobile data transfer. When a person moves with the phone turned on, the device will invariably receive a signal from the nearest tower, that is, switch between them. This way the connection will always be good. The exception is when something interferes with the signal - for example, you are in a basement where no additional equipment is installed, or you have gone out of town and the nearest station is quite far from you.
Quality of communication in the regions
The network and its coverage in remote areas of the country and specific regions is at a lower level. In most cases, 3G is available, which is usually sufficient for Internet surfing and full use of the mobile network.
In small towns and villages, high-speed Internet LTE 450 can be used, which is connected using special equipment.
Since the map does not take into account additional factors (number of towers, etc.) that could affect the connection, it makes no sense to rely solely on it. The error also includes the number of subscribers in a particular location. The network is always better where there is greater demand for it.
Cell phone towers
Cell phone towers are used away from urban areas. In megacities, base stations are placed on the roofs of houses. Their range of action reaches 3-5 kilometers. And around roads, near rural settlements, special towers are installed. As a rule, these are white and red pillars, towers, on top of which a base station is mounted. When there are no forests or reinforced concrete structures in the signal path, towers can be placed at a distance of 10-15 km from each other.
As the mast rental market grows, the landscape is changing rapidly.
How to install cell towers, and what is the price?
Cellular towers are used where there are no other options for placing base stations. Even around villages you can find tall structures on which it will be cheaper to mount antennas than to install a tower. These could be pipes, elevators and other types of high-type buildings.
The requirements for installing a tower are quite complicated:
- the height of the original tower should be from 72 to 100 meters;
- It is advisable to choose the highest place in the area; any hill or hill will do;
- access to electricity is required. If it is not there, you need to install a separate transformer;
- The tower should be installed near populated areas or roads with high traffic capacity.
The intensity of construction of towers is high; for example, in the Moscow region, several dozen of them are installed during the warm season.
The cost of building one cell tower is about 5 million rubles. Recently, it has become common to rent land for such structures not only from legal entities, but also from individuals. True, the rates for private landowners are purely symbolic - several hundred rubles per year.
What are the forecasts for the future?
In anticipation of the emergence of new 5G networks with increased capacity, all operators are preparing to modify their base stations.
MegaFon and Beeline actively cooperate with Huawei, the main supplier of 5G equipment around the world.
MTS works with Ericsson, and Tele2 works with Nokia.
Back in 2021, all operators successfully conducted tests related to preparing for the introduction of 5G. Moreover, MegaFon showed the best results: the speed of data reception using the new technology in the networks of this operator reached 35 Gbit .
MTS, together with Ericsson, showed the maximum speed on test equipment in the region of 25 Gbit .
Beeline, despite its partnership with Huawei, reported speeds of more than 1 Gbit/sec .
Considering all the facts, MegaFon will be the first to launch 5G in Russia . This is facilitated by the largest number of base stations and cooperation with Huawei.
The arrival of the next generation cellular network is only a matter of time. The operators are already ready for it.
(
4.37 out of 5, rated: 38)
Cell Tower Manufacturers and Suppliers
Most tasks related to the construction of cell towers can be solved by Russian companies and suppliers.
There are several companies that have proven themselves in this area:
- Metal-System LLC: the company produces towers, masts, and pipe stands for mounting base stations on the roofs of buildings.
- Altaystroydiagnostika LLC helps to build a tower based on a mast or tower in compliance with all technical and legal requirements. The company's experts know how to properly install supports and ensure uninterrupted operation of the equipment.
- The metal structures plant "Spetsstroykomplekt" can produce a tower according to standard drawings or taking into account the wishes of the customer. Here you can order additional options for the tower: lightning rod, platform for technical personnel.
- MKTEK company is considered one of the cheapest manufacturers of cell towers. The towers installed by this company have a sectional structure. Depending on the required height of the mast or tower, you can choose a different number of sections. This saves money for those customers who plan to install a tower on a hill and who do not need the maximum height of the structure.
The total number of enterprises in Russia that produce and supply equipment for the installation of cellular towers is several dozen companies. The market is so developed that consumers have the opportunity to choose a company that will suit them in terms of the time frame for manufacturing and installation of the tower, the cost of the work, and the features of the technical equipment of the tower.
Tele2 base stations A simple story about complex thingsThis article is intended for the most inquisitive Tele2 subscribers who want to know in general terms how modern mobile communication networks function. We will tell you about base stations and the basic principles of building modern mobile networks.
Each base station of the Tele2 operator, as well as any other cellular operator, is a whole complex of quite complex and very diverse radio equipment. All elements of this complex constantly interact with each other to ensure uninterrupted operation of cellular communications 24 hours a day and 365 days a year.
The most visible part of the base station is the external transmitting and receiving sector antennas, which can most often be found on the roofs of various buildings, chimneys and special antenna structures.
Base station antennas on a building in the Center of St. Petersburg.
Sometimes base station antennas can be seen on more exotic designs. For example, the photo below shows not two palm trees at all, but cell phone towers disguised as them in a resort area of Egypt. If you don't look closely, you may not notice the fakes.
Tele2 uses telecommunications equipment from Nokia Networks and other major manufacturers in its network, including energy-efficient and compact Flexi Multiradio base stations
last generation.
Using only modern equipment will allow Tele2 to smoothly migrate from gradually aging GSM 1800 networks to networks of the most advanced LTE standard in the future (read more about frequency conversion and the transition to LTE in an interview with Tele2 Russia technical director Ritvars Krievs).
Along with antennas, special radio relay stations can often be seen on racks, which ensure the integration of the base station into the cellular operator’s network.
Currently, more than 90% of Tele2 base stations are connected to the network via radio relay communication. However, with the transition to LTE and 3G standards, which imply providing customers with Internet access at high speeds, high-speed fiber-optic communication channels will be supplied to key base stations.
All other base station equipment is located, as a rule, at some distance from the antennas and is located either in non-residential premises of the building on which the BS is installed, or in special containers if installation in the building is not possible.
Modern equipment for base stations is so compact that it can fit in a case similar to an enlarged system unit of a regular computer (take, for example, the already mentioned Flexi Multiradio BS).
Flexi Multiradio base station equipment.
To improve indoor communication and increase the coverage area of BS, signal amplifiers were often used in the past. “Now Tele2 is moving to distributed BSs, in which the radio module is located next to the antenna and delivers its maximum power to it; in addition, losses in the opposite direction are also reduced. Moreover, such assemblies can be moved from the general BS control module to a certain distance - for example, they can be placed along the perimeter of the roof of a building” - Ritvars Krievs.
Coverage area
each base station depends on many different factors. The “range” of a base station is most strongly influenced by the height of the transmitting and receiving antennas, the terrain and the density of urban development. However, one should not think that to ensure good coverage the operator only needs to hang the antennas higher and turn on the transmitters at maximum power. In many cases, engineers deliberately limit the range of individual base stations. For this purpose, different types of BS are used: macro-, micro-, pico- or femtocells. This happens especially often in densely populated areas, where the need to ensure maximum cellular network capacity comes to the fore.
Microcells are used to cover relatively small areas. In the photo: Peterhof. The antennas are installed on the fourth floor of the administrative building and provide local coverage of the park.
For example, to provide sufficient coverage in an abstract urban area, one base station ( macrocell)
). However, as the operator's subscriber base grows, the number of residential subscribers in the coverage area of this station can significantly exceed its maximum throughput. And then, during the “peak” load, most subscribers will definitely have problems dialing (the familiar “network busy” message appears on the screen).
In this case, the operator installs several additional base stations, placing them at low altitudes and in areas of greatest load. Thanks to the uniform distribution of base stations in a densely populated area, an increase in network capacity and a reduction in the load on each station individually is achieved. Such BSs are called microcells
. The coverage area of a microcell, as a rule, does not exceed 1 kilometer, and in densely built conditions it can be only 300-500 meters.
To avoid interference that can occur with such a dense location of stations and limited frequency resources, all operators are forced to resort to complex frequency planning of their networks.
If the operator needs to locally cover an area with maximum voice or Internet traffic (this could be a busy area near a metro station or an intersection with constant traffic jams), low-power microcells
, which are installed directly in areas of concentrated traffic. The antennas of these base stations can be located only three to four meters from the ground, on low buildings and even, sometimes, on street lighting poles.
In large cities, operators solve another problem - high-quality coverage of key subscriber concentration areas in enclosed spaces. These can be shopping and business centers, metro stations, hypermarkets and other urban infrastructure facilities. Ensuring high-quality and uninterrupted communication in such places is a task of paramount importance. Here, a special type of compact base stations, the so-called, comes to the aid of operators. picocells
, which provide the necessary quality of reception and network capacity in indoor areas. In some cases, instead of a separate base station, repeaters are used that relay and amplify the signal of an external BS inside the building.
Cellular antennas in the subway.
Outside of major cities, the maximum range of each base station comes to the fore. To do this, antennas are installed on the highest masts, the directional action of sector emitters is adjusted (which is especially important for BS installed along highways and railways) and, if possible, use longer-range frequencies in the 900 MHz range. The coverage area of such a station can reach 32 km in normal operation.
Unfortunately, TELE2 in most regions has licenses only for frequencies in the 1800 MHz range, which leads to an increase in the cost of covering suburban areas - the range of BS operating in the GSM 1800 range does not exceed 5-6 kilometers, which forces the operator to install a larger number of BS than in case of using GSM 900.
Installation of such base stations located at a serious distance from civilization is associated with high costs on the part of operators. It is necessary to lay many kilometers of power lines, construct access roads, install expensive towers and equipment in difficult hydrogeological conditions (helicopters are often used for this) and ensure uninterrupted operation of the BS in remote areas. Thanks to this complex work, we can use mobile communications even in the most remote and isolated places.
“Harm” from Base Stations
Unfortunately, there is still a common misconception in society about the inevitable health problems that supposedly arise in people from the intensity of the electromagnetic field created by base stations. It is especially common to hear about the dissatisfaction of residents of residential buildings where these same BS are installed. Moreover, complaints about the operation of antennas often begin to arrive even before the actual launch of the station.
BS antennas opposite a residential building.
Meanwhile, residents of houses with installed BS receive the least amount of “radiation” due to the directional action of sector emitters (they practically do not “shine” directly “under themselves”). However, residents of neighboring houses also have nothing to worry about - when putting the BS into operation, the maximum standards for the electromagnetic field from them, established by SaNPiN, are necessarily calculated. And these standards in Russia, it should be noted, are much more stringent than those adopted in many other countries.
Computers, radiotelephones, microwaves and other home appliances, not to mention a cell phone pressed to your ear, create significantly more electromagnetic “noise” in our homes than BS antennas installed somewhere outside the window. To effectively reduce the level of electromagnetic field generated by a mobile phone, you just need to hold it correctly in your hands.
- Never cover the top of the device with your palm - this is where the transmitting and receiving antenna is located in most cases;
- try to move closer to the windows during a conversation, even if an acceptable network level is provided indoors;
- the better the network catches, the less the cell phone transmitter emits;
- We recommend turning off Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and the Internet connection immediately after using them.
To effectively reduce the electromagnetic field strength at home
, stick to a few healthy habits, many of which will also help reduce your electricity bill.
- Turn off the Wi-Fi access point at night or if you do not plan to use it for a long time;
- do not place the DECT radiotelephone base station and Wi-Fi router in living rooms; the best place for them is the corridor;
- do not keep electrical appliances plugged in if they are not in use, buy a surge protector with the ability to turn off appliances individually and turn them on only when needed;
- do not keep mobile phones or cordless phones at the head of the bed;
- Many cordless phone models have special eco-functions that reduce the activity of the radio transmitter, for example, ECO-mode in Gigaset phones.
I would like to especially note the fact that in urban areas, operators almost never turn on the transmitter at maximum power, for the reasons stated in the article. In addition, the power with which the transmitter operates greatly depends on the load on the BS. Base stations outside the city, which typically operate at full power to ensure maximum range, are located on high masts, which completely eliminates any harmful effects of radiation on the human body .
Thus, of course, there is no and cannot be any harm from properly installed base station antennas, unless, of course, you are having a picnic on the roof directly under the panel emitter pointed at you. However, this topic is worthy of a separate discussion, so we will talk in detail about the imaginary harm of base station antennas next time.
***
We will be happy to answer all your questions and criticism regarding this article in a special topic on the Tele2 forum. We invite you to familiarize yourself with all our photographs of TELE2 base stations, some of which were used in this article.
© Photos: tele2life.ru and Nokia Siemens | Text author: t2
Tower maintenance
Maintaining towers is not cheap. Equipment must be changed at an uncertain frequency. Some towers work longer in an unchanged condition, others quickly fail. It depends on the type of equipment and the average cell load.
Sometimes tower owners replace the equipment with more modern ones. 4G networks are gradually spreading throughout Russia. Behind this simple phrase there is a huge amount of work involved in upgrading equipment.
Simple maintenance of towers without modernization costs approximately 5% of the cost per year, that is, 250 thousand rubles.
In GSM standard
Naturally, the reception and transmission frequencies are presented in a generalized standardized format of 900 and 1800. In fact, they differ on average: 889 – 999 and 1710 – 1899, respectively, with minor fluctuations in one direction or another. These frequencies are divided between operators in order to avoid difficulties in signal transmission and subsequent tariffication of the services provided. Due to the emergence of the operator in question as the last one on the telecommunications services market in the Russian Federation, the company received only frequencies in the 1800 standard (Tele2 gsm 900 is not used): 1710, 1725, 1778, 1784, 1805, 1820, 1873, 1879 MHz. These Tele2 frequencies are used in all regions of Russia except Moscow.
How to mute TELE2
With the advent of the new operator TELE2, a new task appeared - how to jam it. Let's look at what frequencies does this operator operate at?
In Moscow and the Moscow region, Tele2 has built a network using third and fourth generation technologies. 3G (UMTS) at 2100 MHz , 4G (LTE) at 800 MHz (band 20) and 2600 MHz (band 7). That is, to suppress it, you need to choose this equipment. Unfortunately, other options will be powerless against this operator.
The official launch of the Tele2 operator in Moscow, according to the latest data, was announced on October 22, 2015.
Well, God willing! It seems to me that, to some extent, the operator will adhere to its loud slogan, because it is known throughout Russia precisely in the role of an “honest discounter” and people simply do not need it in any other person. However, now Tele2 is a subsidiary of Rostelecom (“T2 RTK Holding”), the owner of the frequencies, and the latter is, let’s say, a state-owned company. Will many of you trust our state and government now? Especially in light of the stage of “standard of living” Russia is currently at.
There is also a bright side to the coin. We have less and less money, but the state still has it. Many billions of rubles are pouring into the Tele 2 network. Accordingly, in this situation, there are quite a lot of chances to get an acceptable quality network at the initial stage. There is also faith in the prospects for the further Napoleonic development of Tele2 in the capital (surely you have noticed the appearance of many lamp posts with antennas on the street? Such posts often belong to Tele2 - at least with humming equipment). I hope this helps with the quality of his service as well. The chaos and confusion of the “Big Three” are perhaps now the main points that make us think about the “honestly cheaper” Tele2. Frequencies and coverage As everyone knows, Tele2 did not have 2G (GSM) frequencies in Moscow. There are only 3G (including for voice) and 4G. This is not gud. The fact is that GSM has a longer range, especially GSM-900.
Do you remember how, at the dawn of MegaFon’s establishment at MSC, they scolded it for poor indoor coverage and attributed this to the lack of 900 frequencies? As a result, MegaFon not only included the EGSM range (an extended 900 frequency range, not supported by all phones at that time), but also began to build its network more densely - installing base stations more often and lower. As a result, MegaFon's network turned out to be of decent quality, comparable to its competitors, and in some places even better. Then came 3G and LTE. But only due to them, it is even more difficult to make high-quality signal penetration into the premises. Especially in basements and with thick walls. Therefore, ideally, it would not hurt for Tele2 to additionally become someone’s MVNO (virtual) operator in Moscow in terms of GSM support.
By the way, Tele2 will not work in this form on phones without 3G (simple dialers) in Moscow. But personally, sometimes I want to take a break from modern technology and the Internet by moving the SIM card into the simplest phone only for calls and SMS. It is important. You can buy a new SIM card for your phone, but not everyone will buy a “phone for an operator.” Now Tele2 is trying to make its network as acceptable as possible before the launch, which is why its launch has already been postponed. This is no longer the time when you can afford to launch a leaky network, ruining your own image for many years.
Tele2 wants to start in Moscow and the Moscow region with more than 3,000 base stations. Free calls? Allowing yourself to fantasize, it is logical to assume that the future of Tele2 is the implementation of free voice communications using VoLTE and VoWi-Fi technologies with the main source of income based on the mobile Internet. True, this is no longer know-how, but honestly the rules of tomorrow (or is it today?) are still followed by operators with great difficulty and reluctance. Tele2 tariffs in Moscow It is expected that the operator will start its start with the “Black”, “Very Black” and “The Blackest” tariffs - with packages of Internet, SMS and minutes, as well as free vrutreenetwork on the junior offer for a reasonable subscription fee. There are no similar information about the parameters of tariff plans for Moscow and Moscow Region yet; you can familiarize yourself with the already released options for St. Petersburg and the launch of the Tele2 network in other regions of Russia.
Points of sale Of course, there is an opinion about the importance of a large number of Tele2 sales points and showrooms within walking distance both in Moscow and in the Moscow region. This is especially important at the initial stage of new connections. But, having a good budget, the “fourth operator” now allows itself to make very tasty offers to owners for renting premises. So everything is going quite optimistically here. Conclusions Why does our state need its own operator? That's the question. After all, it already controls the communications sector and the Internet, including public Wi-Fi (why did they come up with identification?), monitors and manipulates people by their behavior on social networks and the global web in general, conducting its propaganda, right? However, given the disgrace that the Big Three operators are doing here, oddly enough, one more player in Moscow will only benefit us. This is my opinion.
Russians' struggle with mobile networks
The operator Tele2 has repeatedly faced protests from Russians against its communication towers. For example, on June 22, 2021, residents of the village of Chudinovo (Vladimir region) spoke out sharply against the installation of its tower on the territory of their village. They stated that Tele2 decided not to coordinate the installation of its building with them, and moreover, a team of workers began construction at 4 a.m. literally a few meters from one of the residential buildings.
Chkalovsk is far from the only settlement whose residents are disturbed by operator towers
Three days later, on June 25, 2021, the fierce enemy was seen in the Tele2 tower by those living in the village of Shcherbinino, Stupinsky district (Moscow region). They staged a mass protest, citing the fact that the territory had not been demarcated. The structure was planned to be located less than 100 meters from the nearest residential building, and village residents began preparing an appeal to the prosecutor's office.
Not only Tele2 faces protests from local residents regarding towers, but in a number of cases the authorities take the side of the residents. This happened with the operator MTS - in the spring of 2021, it installed a tower in the center of the private sector in the Ordzhonikidze district of Perm. Residents went to court demanding the demolition of the structure, but initially the decision was made in favor of MTS. After this, the Russians filed a complaint with Roskomnadzor, and this had an effect. In June 2021, MTS received an order to dismantle the installed tower.
What happens if seven of the eight controllers are removed from the SDH?
Infrastructure
However, such disputes in Russia are not always resolved by legal methods - more often citizens use faster and more accessible methods, although not at all legal. For example, in May 2019, a 53-year-old resident of the Sverdlovsk region tried to burn down a cell phone tower, not wanting to be exposed to radiation. The tower was located in the village of Kalya, Sverdlovsk region. A criminal case was initiated against the arsonist under Art. 47 of the Criminal Code of Russia “Deliberate destruction or damage to property”, and she faces imprisonment for up to five years.
Also in May 2021, an elderly man living in the Tver region committed lynching over a cell phone tower. He sawed off the support of a tower, the radiation of which, as it seemed to him, was destroying the harvest of vegetables, berries and fruits on his plot, located nearby. A sawed-off communications tower fell onto the wires of a nearby high-voltage line, leaving nearby settlements without power.