What is the difference between LTE, 4G and 3G
find 10 differences
4G and LTE in questions and answers
Even a first-grader today knows how to use the mobile Internet. Developed wireless technologies allow you to access the network not only from computers and laptops: most phones, players, tablets and other gadgets have Internet access. For the average user, the communication standard is unimportant: it is not necessary to know the difference between 3g and 4g and what lte means in order to download applications, view news feeds on social networks and watch movies online.
These questions become more significant when studying the characteristics of the mobile Internet. What do the lte and 4g standards provide and what is the difference between them?
What is 3G and 4G
Within the 3rd generation of communication, the data transfer rate is 384 Kbps. Having opened the general settings of the device, the user will see the UMTS option, which indicates compatibility with the 3rd generation network. The coverage map covers the entire country. This made it the most popular among subscribers of various operators.
At the moment, all residents of large cities have access to the 4 generation communication network, which is also called LTE. By connecting to it, the user will be able to appreciate the benefits of the connection and high data transfer speed, which is 100 Mbit/s. Before switching to this standard, you should definitely check your device for compatibility. If a mobile device does not have a 4G function, the owner of the device will not be able to connect to the network of the required format.
Having studied all the advantages and disadvantages, you can understand what is better than LTE or 3G.
Is there a difference between them or not?
As I indicated before, 4G is an abbreviation that can be deciphered - 4generation (4th generation).
4G samples can be considered:
- LTE;
- TD-LTE;
- Mobile WiMAX;
- UMB;
- HSPA+.
Of these standards, the LTE format has gained the most popularity in the Russian Federation. Interestingly, for its availability there is no need to create new communication stations; it can be used with 3G equipment. This format is available in most cities in the European part of Russia.
3G and 4G: what is the difference
By studying the connection parameters of various networks, you can correctly understand the difference between 3G and 4G. The third generation provides the user not only with access to the global network, but also with a certain set of functions for communication. This communication standard is based on packet data transmission.
The transmission speed reaches 3.6 Mbit/s, which allows owners of mobile devices to perform the following actions:
- visit pages of Internet resources using a computer;
- view mail;
- communicate via instant messengers;
- view pictures;
- download small files.
Within this network, the user can easily listen to music or watch videos online.
The 3rd generation communication network is represented by the following standards:
- UWC-136;
- DECT;
- TD-CDMA/TD-SCDMA;
- CDMA2000/IMT-MC;
- UMTS/WCDMA.
The last 2 technologies are most widespread.
To understand the difference between 4G and 3G, the user needs to study the advantages of the new network format. The increased requirements of the 4th generation network explain the high-quality Internet connection without dropouts, as well as high data transfer speeds.
The main difference between 3rd and 4th generation networks is the difference in speed between 3G and 4G:
- The 3rd generation network does not allow you to watch movies and videos in high quality, but with 4G this is easy to do;
- 3G has data transfer speed limits, and the 4th generation network provides high-speed Internet to the user;
- within 3G, many Internet services do not work correctly, but 4G does not have such problems.
These operating features help you understand how 3G and 4G Internet differ. The new communication standard provides almost unlimited possibilities when connecting to the Internet.
What is LTE in a smartphone?
Users are wondering “What is LTE support in a smartphone?” LTE is supported by most modern gadgets. But not all users are aware of the capabilities of the system and the specifics of its use. Translated from English, the abbreviation LTE (Long-Term Evolution) means long-term development. The development relates to communication standards, thanks to which the user is able to quickly and without unnecessary connections receive and transmit information. The volume of information is not limited; communication provides a high-speed Internet connection and fast interaction between users.
LTE is more of an intermediate transition from 3G to 4G, but developers note high speed, ease of connection, faster loading and unloading of materials, files, information and documents. Despite updates and continuous improvement of standards, LTE is gradually being replaced by the fourth generation of communications. Very soon, 5G towers will be available to users, but LTE will remain a popular way to work with information flows and data.
Features of 3G operation
The third generation of communications uses high-speed data transfer technology, Internet access and mobile communications. The successful combination of capabilities explains the widespread and popularity of this standard.
Today, all mobile devices can connect to this network; the user only needs to select a suitable SIM card. Additionally, cellular operators provide special mobile modems that allow you to connect any device to the Internet via a wireless network.
To understand which is better, 3G or 4G, the user needs to pay attention to the capabilities of these networks.
The undeniable advantages of 3G include the following factors:
- 3G is more stable than 4G;
- multi-level data protection;
- excellent territorial coverage that covers the entire country;
- sufficient speed for video calls, work and communication;
- personal IP address.
The disadvantages of this communication format are the speed limit, as well as its drop while driving. To compare 3G and 4G networks, the user should definitely take into account all the positive and negative aspects. This will allow you to choose the right communication format, which will be the optimal solution in specific conditions.
4G Features
Today, many subscribers are wondering which is better, LTE or 3G. At the moment, increasing the coverage of 4th generation networks is called the main task of providers.
Before switching to this communication standard, the user needs to understand:
- which is faster, LTE or 3G;
- whether the house is within the network coverage area;
- Does the mobile device support 4G function?
Due to the increased requirements, 4 generation networks have a number of positive characteristics:
- The difference between 3G and 4G Internet is IP telephony. This function is not available on the 3rd generation network. The 4G standard allows you to communicate without voice delays.
- The big difference between 3 GI and 4 GI is expressed in the range of Internet signal reception. By connecting to a new generation network, the user will be able to transfer data even at a great distance from the base station.
- Difference in 4G vs 3G speed. The 4th generation communication format provides the subscriber with high data transfer speeds, the rate of which reaches 100 Mbit/s.
- Modern models of mobile devices allow you to automatically select the operating mode. If there is a loss of 4G signal, the smartphone will switch to 3G mobile Internet.
When choosing LTE or 3G, you need to take into account your personal needs, as well as the capabilities of your device. The 4th generation standard maximizes user capabilities, which indicates its thoughtful operation. It can be called a natural continuation of 3G, which has improved performance, high data transfer speeds, and stability. These criteria allow you to quickly understand which is better, 3G or LTE.
Where did 3G come from?
With the advent of the first portable telephone, wireless networks emerged. Until there were modern standards, 1G and 2G were used. As these technologies developed, the data transfer rate increased from 2 kbit/s to 10-15 kbit/s. This allowed the exchange of short text messages (SMS).
The increase in the number of users pushed to improve GSM standards. After all, accessing the World Wide Web through mobile equipment was problematic and came down mainly to adapting Internet pages using WAP technology.
A new stage of development was the emergence of GPRS and EDGE standards (2.5G and 2.75G). Communication has become faster: up to 50 Kbps-1 Mbps. With such indicators, Internet surfing has become accessible, but it is still not as high-speed and familiar to today’s user.
3G standards and speeds
The birth of the third generation became available with the advent of CDMA technology. Since 1995, new 3G standards have been created on its basis, and other 3G frequencies have been used.
- CDMA2000, operating at a frequency of 1250 MHz, develops data transmission up to 1.8 Mbit/s.
- WSDMA – covers the 3G frequency range 1900 – 2100 MHz, data transfer speeds up to 2 Mbit/s.
In Europe and Russia, other directions are very popular:
- UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) operates in the frequency range 2100 – 2200 MHz. The maximum 3G speed is 21 Mbit/s, but the practical figure ranges between 384 kbit/s and 7.2 Mbit/s.
- HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access - high-speed packet access) and HSPA+ (Evolved High-Speed Packet Access - developed high-speed packet access) the emergence of these technologies opens up the opportunity to download files at 14.4 Mbit/s and 21.6 Mbit/s. When buying previously popular modems, you can see the wording 3.5G, and when using a smartphone, the letter “H” or “H+” is displayed above the network indicator.
- DC-HSPA+ essentially doubles the transfer speed to 42.2 Mbps, which is dual-link HSPA+. It is compared to 4G, since Internet usage indicators are comparable to those produced by 4G on average.
Activating 4G on Android devices
To successfully enable the service on a mobile device, the user must:
- Buy a SIM card with connected 3G and 4G mobile internet service.
- Check the 4G coverage map of a specific provider.
- Make sure that the device supports the desired function.
The gadget is checked through the basic settings of the device. The main difference between a 3G modem and a 4G modem is the ability to connect to a new generation communications network. If the device does not have such a function, the user will not be able to take advantage of high-speed Internet capabilities.
Why was 4G displayed before, but now 3G: possible reasons
You set up 4G, but after a while 4G stopped being displayed, and 3G is displayed again? Before going to the service center, check out the most common errors:
- The LTE radio module has turned off. Plug it in again;
- 4G settings have been deleted. Repeat the connection as for the first time;
- There is no 4G coverage where you are currently located.
If you do not find a solution to the problem in this list, contact a specialist who will help solve the problem.
Switching 3G to 4G
This transition does not require changing network settings. Activating 4G will allow you to connect to high-speed Internet.
To switch to a high-speed network, the user must perform the following operations:
- Open the main settings menu of your phone or tablet.
- Go to the Mobile networks section.
- Open the More item and go to the Other networks subsection.
- Select Mobile networks.
- Open the Mode item.
The user needs to specify the appropriate connection type. You need to understand that if the communication standard you are interested in is not on the list, the device is not equipped with the required function.
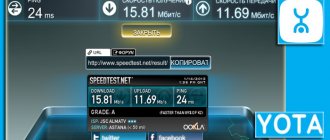
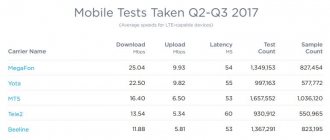
Tests of wired and wireless Internet:
Tested Akado and Megafon 4G
speed check through services:
Speedtest (RuTube server)
(D: 22.63 Mb/s, U: 21.07 Mb/s)
(D: 39.75 Mb/s, U: 1.92 Mb/s)
2IP
(D: 4.61 Mb/s, U: 5.10 Mb/s) (D: 34.69 Mb/s, U: 1.84 Mb/s)
Host-tracker Speed Test
(D: 15.11 Mb/s, U: 4.75 Mb/s) (D: 12.48 Mb/s, U: 6.12 Mb/s)
YouTube video upgrade:
(1080p HD full screen, 100Mb file) measured with a stopwatch. megaphone 4g (time: 02:02) akado (time: 02:05)
downloading a torrent file:
megaphone 4g (file 599.9 Mb) (time: 02:12) (peak speed: 6 megabytes per second) akado (file 597.1 Mb) (time: 02:17) (peak speed: 5.1 megabytes per second)