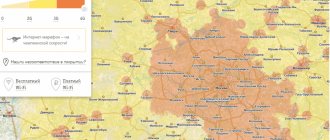
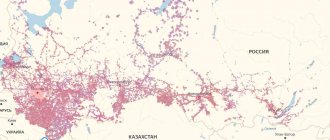
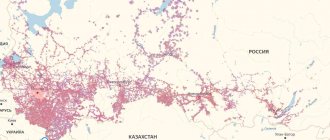
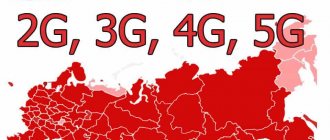
MTS is constantly increasing the number of base stations, which has allowed it to create a modern telecommunications network. Today, the MTS coverage area is recognized as the most extensive, which guarantees the availability of mobile communications even in the most remote regions of the Russian Federation.
MTS cellular communications support several generations of networks, ranging from 2G to 4G. Thanks to this, subscribers can be confident in high-quality communications, both in their home region and beyond, as well as high Internet speed.
Office Pro Kit
RF-Link repeater, Internal antenna, External antenna, Cable, Connectors
from 73655 rub.
More details
The coverage area is designed to help you choose the best quality operator in your region. The map is current and updated automatically.
Yota operator is a virtual operator of Megafon and operates at its base stations. Therefore, Yota’s coverage map completely coincides with Megafon’s coverage.
The Beeline coverage map is displayed conditionally, because The coverage map is stored in a format different from Yandex maps.
Generations of base stations and their coverage radius
Each operator has a wide network of 3G (third generation) and 4G LTE (fourth generation) base stations. If you have not yet decided on the choice of operator or want to switch to another, you may be interested in the map of cellular base stations of the operator you need, which will show in detail the coverage area. The range of one station depends on the location and frequency range. 3G stations in megacities reach 500m, in open areas - up to 35km. 4G LTE stations - the radius can be different, optimally it is about 5 km, but if necessary it can be up to 30 km or even 100 km (if the antenna is raised sufficiently).
Mobile operators have learned to combine low and high frequencies. For areas where a small number of subscribers live, but they occupy a large area, networks operating in low bands are ideal. And in large and densely populated cities, high-band networks are being built. Dual-band LTE networks are the future of mobile communications.
How does a base station work?
- The first thing that catches your eye is the transceiver antennas. They are placed on the roofs and walls of buildings, on pipes, and can be on special structures, lanterns, and even on exotic structures (in Egypt, they are disguised as palm trees).
- Radio relay stations in the form of dishes for connecting a base station to a telecom operator's network via radio relay communications.
- Base stations of the 4th and 5th generations - high-speed fiber-optic communication channels are connected to them.
- Related equipment - climate control systems, power supply, ventilation, security, cellular amplifiers, etc. in the building itself or nearby, in special containers or enclosures.
There is an opinion that if there are many antennas, and they are high, and the transmitter works “to its fullest,” then the connection will be better, but this is not so.
The coverage area of some base stations is often deliberately reduced. Various types of base stations are used:
- macro cells with a range of up to 100 km.,
- microcells with a radius of up to 5 km.,
- picocells or femtocells, which are installed in areas with high population density (shaped like a laptop).
Base station communication:
- Small base stations transmit signals to each other via a fiber optic cable system.
- Large base stations that cover long distances communicate with each other through radio relay dishes.
Roskomnadzor reported that the Big Four operators continue to increase the number of base stations in Russia. In the first half of 2021, there were already 624,800 base stations of all mobile operators, which is 9% more than in the first half of 2021.
Megafon has the most base stations in Russia, more than 209,573 of them. In the first half of 2021 alone, 13,005 stations were installed. MTS takes second place - 161,607 (plus 9,654 BS for 6 months of 2018). Beeline is in third place - 130,841 BS (plus 20,625 stations for 6 months of 2021). And in fourth place is Tele2, they have 122,823 base stations (plus 6,868 stations for 6 months of 2021). The construction of base stations is a complex and labor-intensive process, which includes:
- Selection of a site and conclusion of a lease agreement.
- Design and survey work.
- Registration of permitting documentation, sanitary and epidemiological conclusion on the safety of the station for others, documentation for equipment, for metal structures.
- Production of antenna support structures.
- Construction of the foundation.
- Installation of metal structures of masts.
- Manufacturing and installation of equipment containers.
- Installation of antenna-feeder devices.
- Installation of base station equipment and electronic control unit.
- Power supply connection and commissioning.
Feederless base stations have recently begun to be used. They reduce the cost of equipment and its installation; they are used for communications in 3G format.
Base stations are often installed on the roofs of residential buildings. This is permitted by law, but certain rules must be followed:
- The electromagnetic field level (EMF) in the adjacent area should not exceed 10 mW/cm2;
- the antenna should be erected at a level of 1.5 to 5 meters from the roof surface and at a distance of 10–25 meters from other buildings;
- The ability of people to access the roof should be limited.
- The placement of a base station occurs after a meeting of the owners of the premises (in accordance with Article 44 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation), and at least 1/2 of the residents must vote.
Many people believe that cellular operators are raking in billions without investing their funds, but this is not so.
Operators invest money in the construction of cell towers and the installation of base stations. They spend money on a license for frequencies (2G is more expensive than 4G), on rent, maintenance and maintenance of the BS.
Unusual.
- African operators are installing cellular base stations in rivers on special rafts. This increases the coverage area of nearby villages and the river itself. Due to the lack of roads, all main transport routes are by water. It also reduces the likelihood of equipment theft.
- Base station in the Lefortovo tunnel in Moscow. Antennas are slotted radiating cables.
- Base station powered by solar energy in the Krasnodar region and Western Australia.
- In the UK, in the center of Aberdeenshire Forest, an autonomous base station with a power source based on hydrogen fuel cells has been installed. The same station is installed in Scotland, near the ski center.
Using the coverage area of cellular operators
This coverage area is convenient for a preliminary analysis of the possibility of connecting to 3G/4G Internet. Data is provided by cellular operators and is generated through virtual calculations rather than measurements. Therefore, you need to understand that there is a fairly large error here.
If you are 2-3 kilometers from the edge of the 3G/4G coverage area, then to install an antenna to strengthen the cellular signal, it is strongly recommended to hang the antenna on a mast 4-6 meters high.
The towers of cellular operators MTS and other operators can be determined quite accurately - they are located in the center of the coverage area of small areas. Or install the “Cell Towers” program on Android and when launched, the program will immediately indicate the exact location of the nearest cell operator tower.
Tele2 is a subsidiary of Rostelecom , i.e.
Where Tele2 coverage is available, Rostelecom SIM cards will also work there.
Yota coverage map
This is a relatively new provider, with the first 4G frequencies in Russia. It was formed in 2006. And already in 2008, the first fourth-generation Wimax network in Russia was launched. After a long journey and through trial and error, the decision was gradually made to switch to the more promising LTE technology. But now Yota is one of Megafon’s divisions. He is the leader of the "Big Three" cellular monopolists in the country. This company is interesting because it provides large volumes of traffic and a good coverage area.
Go and collect the tariff>>>
Network faults
How long does it take to fix a communication problem if it occurs?
The Operator provides communication services to Subscribers 24 (twenty-four) hours a day in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, national standards, technical norms and regulations, licenses, as well as an agreement on the provision of communication services.
Unless a different period is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, the Operator eliminates malfunctions that impede the use of communication services (hereinafter referred to as malfunctions) within 7 (seven) working days from the date of registration of the Subscriber’s request. Malfunctions caused by the actions of third parties must be corrected within 30 (thirty) business days from the moment the Operator became aware of this. In some cases (force majeure circumstances, major accidents, etc.), the timing of troubleshooting is determined by the Operator individually and brought to the attention of Subscribers by posting information on the Operator’s website on the Internet information and telecommunications network.
Internet access services: Novosibirsk region
In addition to telephone services, the company also provides its subscribers with Internet access. Moreover, the functions of both Internet access from a smartphone and from a tablet or personal computer/laptop are implemented. The packages differ mainly in cost and amount of available traffic. Overall, since Tele2 has to compete with the leading Big Three operators, it has to maintain connection quality and speed at a high level, as well as offer competitive prices for its services.
Tariffs for Internet services Tele2
To write and send a free SMS to a Tele2 subscriberfollow the link above to the official website www.sms.tele2.ru |
In order to combat SMS spam and the sending of messages that deliberately mislead network users,
the sender's IP address and a warning about possible fraudulent activities will be attached to each SMS message sent
Tariffs for sending MMS from the site: the first 5 MMS messages per month are sent free of charge. Further, the cost of each multimedia message will be 50 kopecks, which will be debited from your Tele2 subscriber account.
Using the service “Sending SMS from the official Tele2 website”, you can send free SMS to Tele2 subscribers in the following regions of Russia
: Arkhangelsk, Severodvinsk, Kotlas, Novodvinsk, Koryazhma, Mirny, Velsk. Services are provided by CJSC Arkhangelsk Mobile Networks. Belgorod region: Belgorod, Stary Oskol, Gubkin, Shebekino, Alekseevka, Valuiki. Subscribers are served. Bryansk region: Bryansk, Klintsy, Novozybkov, Dyatkovo, Unecha, Karachev. Bryansk branch of CJSC Smolensk Cellular Communications. Vladimir region: Vladimir, Kovrov, Murom, Alexandrov, Gus-Khrustalny, Kolchugino, Vyazniki. Tariffs and services for subscribers are provided by the Vladimir branch of Votek Mobile. Vologda region: Vologda, Cherepovets, Vologda, Sokol, Veliky Ustyug, Sheksna. Mobile communication services at the specified tariffs are provided by the Vologda branch of OJSC St. Petersburg Telecom. Voronezh region: Voronezh, Borisoglebsk, Rossosh, Liski, Ostrogozhsk, Novovoronezh, Novaya Usman. Jewish Autonomous Region: Birobidzhan, Obluchye, Nikolaevka, Leninskoye. Komi Republic: Syktyvkar, Ukhta, Vorkuta, Pechora, Usinsk, Inta, Sosnogorsk. Kaliningrad region: Kaliningrad, Sovetsk, Chernyakhovsk, Baltiysk, Gusev, Svetly, Gvardeysk, Zelenogradsk. Rostov region: Rostov-on-Don, Taganrog, Shakhty, Novocherkassk, Volgodonsk, Bataysk, Novoshakhtinsk, Kamensk-Shakhtinsky, Azov, Gukovo. Kaluga region: Kaluga, Obninsk, Lyudinovo, Kirov, Maloyaroslavets, Balabanovo, Kozelsk, Kondrovo. Ryazan region: Ryazan, Kasimov, Skopin, Sasovo, Ryazhsk, Rybnoye, Novomichurinsk. Kamchatka Territory: Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Elizovo, Vilyuchinsk, Milkovo, Klyuchi, Ust-Kamchatsk. St. Petersburg and Leningrad region: Zelenogorsk, Kolpino, Krasnoe Selo, Kronstadt, Lomonosov, Pavlovsk, Peterhof, Pushkin, Sestroretsk, Gatchina, Vyborg, Sosnovy Bor, Vsevolozhsk, Tikhvin, Kirishi, Sertolovo, Kingisepp, Volkhov, Tosno, Luga. Kemerovo region: Novokuznetsk, Kemerovo, Prokopyevsk, Mezhdurechensk, Leninsk-Kuznetsky, Kiselevsk, Yurga, Anzhero-Sudzhensk, Belovo, Berezovsky, Osinniki, Myski, Mariinsk, Topki. Sakhalin region: Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, Korsakov, Kholmsk, Okha, Poronaysk, Dolinsk. Kirov region: Kirov, Kirovo-Chepetsk, Vyatskie Polyany, Slobodskoy, Kotelnich, Omutninsk, Yaransk, Sovetsk. Smolensk region: Smolensk, Vyazma, Roslavl, Yartsevo, Safonovo, Gagarin. Kostroma region: Kostroma, Bui, Sharya, Nerekhta, Volgorechensk, Galich, Manturovo. Tambov region: Tambov, Michurinsk, Rasskazovo, Morshansk, Kotovsk, Uvarovo. Krasnodar region and the Republic of Adygea: Krasnodar, Sochi, Novorossiysk, Armavir, Yeisk, Kropotkin, Anapa, Slavyansk-on-Kuban, Gelendzhik, Tuapse, Labinsk, Tikhoretsk, Krymsk, Maykop, Yablonovsky, Enem, Giaginskaya, Adygeisk Tver region: Tver, Rzhev, Vyshny Volochyok, Kimry, Torzhok, Konakovo, Udomlya. Kursk region: Kursk, Zheleznogorsk, Kurchatov, Lgov, Shchigry, Rylsk. Tomsk region: Tomsk, Seversk, Strezhevoy, Asino, Kolpashevo. Lipetsk region: Lipetsk, Yelets, Gryazi, Lebedyan, Dankov, Usman. Tula region: Tula, Novomoskovsk, Donskoy, Aleksin, Shchekino, Uzlovaya, Efremov, Bogoroditsk, Kimovsk, Kireevsk. Magadan region: Magadan, Ola, Susuman, Sokol. Udmurt Republic: Izhevsk, Sarapul, Votkinsk, Glazov, Mozhga, Igra, Uva, Balezino. Murmansk region: Murmansk, Apatity, Severomorsk, Monchegorsk, Kandalaksha, Kirovsk, Olenegorsk, Kovdor. Chelyabinsk region: Chelyabinsk, Magnitogorsk, Zlatoust, Miass, Kopeisk, Ozyorsk, Troitsk, Snezhinsk, Satka, Chebarkul, Kyshtym, Yuzhnouralsk, Korkino. Nenets Autonomous Okrug: Naryan-Mar, Iskateley. Nizhny Novgorod region: Nizhny Novgorod, Dzerzhinsk, Arzamas, Sarov, Bor, Kstovo, Pavlovo, Vyksa, Balakhna, Zavolzhye, Bogorodsk, Kulebaki, Gorodets, Semyonov, Lyskovo, Sergach, Shakhunya, Navashino. Novgorod region: Veliky Novgorod, Borovichi, Staraya Russa, Pestovo, Valdai, Chudovo, Malaya Vishera. Novosibirsk region: Novosibirsk, Berdsk, Iskitim, Kuibyshev, Barabinsk, Karasuk, Ob, Tatarsk, Toguchin. Omsk region: Omsk, Tara, Isilkul, Kalachinsk, Tavrichesky, Nazyvaevsk. Oryol region: Orel, Livny, Mtsensk, Znamenka, Bolkhov, Naryshkino. Pskov region: Pskov, Velikiye Luki, Ostrov, Nevel, Opochka, Pechory. Republic of Karelia: Petrozavodsk, Kondopoga, Kostomuksha, Segezha, Sortavala, Medvezhyegorsk.
MTS towers on the map
As such, a map of radio towers and stations is not of great importance to subscribers. This is due to the fact that the coverage radius of each tower depends on the frequencies used by the operator and its location:
- points using the 450 MHz frequency are capable of covering up to 20 km;
- coverage of 800 MHz points – up to 13.5 km;
- 1800 MHz – up to 7 km;
- 2600 – 3,2.
It is important to emphasize that most Russian operators, including MTS, use universal radio towers that operate in several bands at once. This allows you to avoid difficulties with connecting to 3g and 4g and provide clients with reliable, stable communications.
Another factor influencing the location of towers is the number of subscribers in a populated area. The larger the city and the greater the number of connected users, the more often the radio towers are located. In this case, their number directly affects the operator’s ability to maintain the network.
Top up your account
Topping up your phone account is not difficult and can be done in many different ways, so that any of the company’s clients in the Novosibirsk region can choose the method that suits them. Payment can be made without leaving home, through your personal account or mobile application. You can also link a phone number to a bank card and even set up an auto-payment option, then the account will be replenished automatically provided there are sufficient free funds on the card.
In addition, it is possible to make payments using the most common services that handle electronic money, for example, Qiwi or Elexnet. It is also possible to transfer funds from another phone. You can also top up your account at customer service centers, ATMs and self-service terminals.
Click on the image to see how to replenish your balance