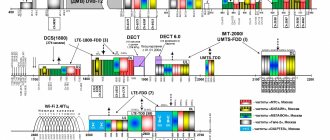
Today, Russian mobile operators are actively expanding the coverage area of fourth generation networks. LTE is a term used to refer to networks with a throughput of at least 10 Mbps. 4G networks are a new communication standard, which is characterized, first of all, by fast connections and high quality voice calls.
List of LTE frequencies used by Russian mobile operators
The 4G networks of each domestic operator are located in a certain frequency range. The presented table contains information about LTE bands (from the English Band), which are supported in our country:
| Band name | Frequency |
| Band 3 | 1800-1880 MHz |
| Band 7 | 2620-2690 MHz |
| Band 20 | 790-820 MHz |
| Band 31 | 450 MHz |
| Band 38 | 2570-2620 MHz |
The LTE standard is not compatible with second and third generation networks, so special data transmission channels were allocated for it. Band is the frequency bands of any LTE network. The band number indicates the period when the given range began to be used in the world (there are currently 44 bands).
The bands presented in the table are used by each cellular operator. It should be noted that these frequency ranges are constantly expanding, which allows providers to provide Internet connections to a larger number of users.
In some cases, operators unite to build cell towers: a similar agreement was concluded in 2021 by Beeline and Megafon. Another example of cooperation was the agreement between Beeline and MTS, according to which the operators use common frequencies in the territory of some constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The acquisition of bend frequencies occurs through open bidding, in which providers buy the right to broadcast their signal on certain channels. MTS, for example, spent 4 billion rubles on the 2500 MHz band, distributed throughout the Russian Federation except the Moscow region and Crimea. Tele2 was the first to launch 4G in the Kaliningrad region and a number of other regions of our country at a frequency of 450 MHz.
4G LTE networks in Russia
Now you can familiarize yourself with the table, which presents the current characteristics of fourth generation networks in the Russian Federation.
| Operator | Frequency (upload/download), MHz | Duplex | Band |
| Yota | 2500-2530 / 2620-2650 | FDD | Band 7 |
| Megafon | 2530-2540 / 2650-2660 | FDD | Band 7 |
| Megafon | 2575-2595 | TDD | Band 38 |
| MTS | 2540-2550 / 2660-2670 | FDD | Band 7 |
| MTS | 2595-2615 | TDD | Band 38 |
| Beeline | 2550-2560 / 2670-2680 | FDD | Band 7 |
| Tele2 | 2560-2570 / 2680-2690 | FDD | Band 7 |
| MTS | 1710-1785 / 1805-1880 | FDD | Band 3 |
| Tele2 | 832-839.5 / 791-798.5 | FDD | Band 20 |
| MTS | 839.5-847 / 798.5-806 | FDD | Band 20 |
| Megafon | 847-854.5 / 806-813.5 | FDD | Band 20 |
| Beeline | 854.5-862 / 813.5-821 | FDD | Band 20 |
In addition to the five federal operators, there are also regional ones, each of which has its own frequency network.
Upper and lower frequencies
From a financial point of view, the development of LTE networks at lower frequencies (less than 2000 MHz) is most profitable for operators. Such frequencies penetrate buildings better, but are not able to provide high-speed connections to areas with high population density.
The functions of the upper frequencies are opposite to the functions of the lower ones, so the best option for a high-quality connection is a combination of both frequency channels, which allows you to get rid of “shadow” areas over large spaces.
Also in megacities, there is a tendency to install special devices on the roofs of office buildings to facilitate the spread of high-speed networks indoors.
Basic LTE modes
The LTE standard is divided into two types: TDD and FDD.
The first implies temporal (from the English Time) division of the signal, and the second - frequency (from the English Frequency). FDD is a more convenient communication mode because, from the point of view of everyday use, it is more stable.
The difference between these concepts lies in the method of loading and unloading data. Thanks to FDD, parallel processing of incoming and outgoing Internet traffic occurs.
Imagine that a user is watching a video on YouTube and at the same time uploading an entire album of photos to the cloud storage. Watching a video will be considered a download operation, and sending a photo will be an upload, and in FDD mode the gadget distributes both operations over different frequency channels.
For example, LTE from the Russian Megafon operates at a frequency of 17 MHz, 11 of which can be used for downloading content, and the remaining 6 for uploading.
Separate traffic processing increases the stability of the speed of each individual process, thereby ensuring a better connection.
TDD processes traffic sequentially. In other words, over the same 17 MHz, both downloading and uploading of data will be carried out - but without separation, but alternately in one channel. The disadvantage of this mode is possible “jumps” in speed.
Currently, Russian cellular operators are striving to combine the operation of TDD and FDD stations. By combining modes into one network, providers increase the overall connection speed.
How LTE affects calls
You can determine for yourself whether the VoLTE function works by the call quality
For calls via high-speed frequency, VoLTE (Voice over LTE) technology is used. Internet access is not disconnected during a call. Subscribers connect with each other faster thanks to the communication standard, and the sound quality improves due to the HD Voice - a technology that creates the effect of the presence of the interlocutor nearby. Typically, VoLTE is enabled automatically when you activate a new smartphone or in the device settings.
4G technology will be relevant for a long time - we hear about 5G almost every day, but this communication standard has yet to be developed. In turn, telecom operators do everything to ensure that the connection speed is adequate; 4G+ is one of the ways to achieve speeds.
LTE-advanced technology (4G+)
LTE-advanced is an “advanced” 4G network and is designated by Russian operators as 4G+. Although this name emphasizes the increase in speed of the new standard, it is not correct, since LTE-A in its actual performance is regular 4G. What is called 4G in Russia is significantly inferior to the nominal standards of fourth generation networks.
The advantage of the advanced standard is the summation of all frequencies owned by the cellular operator, which reduces the “sag” factor in the data transmission channel. By merging several band 7 bands into one, Megafon was able to increase the theoretical connection speed to 300 Mbit/s.
If we add band 3 frequencies to the frequencies of band 7, then the data transfer speed will be 450 Mbit/s (40 MHz + 20 MHz = 300 Mbit/s + 150 Mbit/s). Unfortunately, the actual throughput of advanced channels is lower than declared and corresponds only to nominal 4G standards.
Any cellular operator that has the appropriate license and the necessary equipment can use various frequency channels. Now there is a tendency to expand channel capacity, the volume of which depends on the frequency range. It is also worth noting that to support LTE-A, the user’s device must have special technical characteristics.
What is LTE?
Now let's look at LTE as a separate type of data transmission over the air. The abbreviation stands for Long Term Evolution, which translates as long-term development. LTE is the first stage in the development of 4G at the very beginning of its appearance. The characteristics and capabilities of this network do not meet the requirements of the International Telecommunication Union, however, to attract people, manufacturers use LTE under the guise of full-fledged 4G. Over time, the union approved the use of these two concepts in one label, which is why it exists to this day.
When technologies make it possible to achieve the stated speeds, operators began to offer full 4G (or as the ITU called it - True 4G) for 4G+ or Advanced. Now you know the main difference between 4G and LTE. Also on our website you can find out the main differences between 5G and 4G!
HSPA+ technology can compare in parameters with LTE. Many people probably notice that sometimes when the signal is bad, the H+ icon appears. This type of wireless connection belongs to the third generation (3G) and offers more modest data transfer speeds.
4G speed
It is worth understanding that the actual connection speed almost always differs from the nominal one. The theory does not take into account factors such as landscape, remoteness of cell sites, or the presence of the user in the building - such conditions interfere with the connection and significantly reduce its quality.
The speed of data transfer also depends on the operator’s workload: the more users have access to fourth-generation networks, the lower the speed indicators. The speed of the Internet connection in wireless networks is determined by the width of the frequency range, as well as the implementation of the communication duplex.
These specifications vary by operator. Although some providers guarantee 300 Mbit/s, the average actual speed is only 75 Mbit/s (Tele2, MTS and Beeline).
The already mentioned tandem of Beeline and Megafon recently began the transition to the LTE-advanced standard, which made it possible to increase speed to 160 Mbit/s in some coverage points.
Now such a standard is presented in Moscow and St. Petersburg, but the regions will have to wait a long time for it: the total distribution of 4G+ throughout Russia is now impossible for two reasons.
The first is the cost of the required equipment, and the second (follows from the previous one) is that as the coverage area increases, the load on existing cell towers will increase, that is, the average speed will only decrease.
Since the speed of the connection depends on the width of the frequency range, we can say that today Megafon is in the most advantageous position, which, after absorbing Yota, added channels of the acquired company to its own frequencies.
Theoretically, the Megafon network can operate on a 40 MHz channel and accelerate in FDD mode to 300 Mbit/s, but since part of the channel is given to subscribers of the subsidiary Iota, the actual speed is approximately 100 Mbit/s.
If we compare networks of the third and fourth generations, the latter have several times higher speeds: an average of 80 Mbit/s versus a maximum of 3 Mbit/s. HSPA+ was able to overclock 3G to 45 Mbps, but these figures still lag behind 4G.
How to make mobile internet 4 g
To connect to an operator and use the Internet at the highest speeds, you need to follow these steps:
- decide on Internet provider 4G. To do this, check out the coverage area in your locality and choose the company that offers more complete coverage of the city area;
- purchase a phone that supports the 4G generation;
- contact your mobile operator;
- choose a tariff and purchase a SIM card;
- install it in your smartphone;
- carry out initial settings. This usually happens automatically when you turn on your mobile device.
Now you know how to connect high-speed 4g Internet to your smartphone. Basically, operators offer their customers tariffs with a monthly subscription fee and restrictions on download volume. At the same time, without paying a fee, the Internet does not turn off completely, but only the speed is cut off. Therefore, you can perform minimal actions when working with the Internet (check the weather, read messages) at any time.
In addition to the fact that you can use 4z Internet on your phone, you also have the opportunity to connect it as the main provider for your home hotspot. However, in this case you should be prepared for the following unpleasant moments:
- a wireless connection is more susceptible to provider failures than a wired connection;
- weather dependence;
- the need for 100% coverage in the location of your home in order to achieve maximum speeds;
- Home routers for 4G networks are several times more expensive than regular ones.
Connecting to unlimited 4g Internet is not an option, but a necessity. Especially in large cities of Russia, where technology is gradually spreading in all public places, even in the metro. It is also worth noting that in provincial cities, coverage area maps are gradually being filled with 4G markers.
Further development of LTE
Despite the launch of testing of fifth generation networks in the world, some regions of the Russian Federation still do not even support 3G. In connection with this circumstance, it is worth predicting, first of all, the widespread development of LTE technology. Also, fourth-generation networks represent a non-alternative way of accessing the Global Wide Web in a number of Russian regions, which encourages domestic cellular operators to develop the 4G standard.
In some cases, a wired connection is simply impossible, which contributes to the spread of wireless technologies: the capabilities of cellular stations can be expanded thanks to special signal repeater antennas. The user can independently purchase such an antenna. It is important to consider that each repeater only works with certain frequencies and mode (FDD or TDD).
Speed difference between fourth and third generations
Third generation technology is a mobile standard for information transfer with the possibility of high-speed access to the Global Network and mobile communications. The date of creation is 1999. Despite this, the real implementation and distribution of 3G began later. The popularity of 3G is still the highest among all mobile operators.
How to check MGTS Internet speed: on a computer or phone
In domestic conditions, the coverage area of the 3G standard is much greater than the coverage of the follower. In addition, this greatly affects the actual speed, since 3G operates at its maximum capabilities, while newer communications only work fully in cities.
Today, the only problem with the 3G standard is its lower speed compared to the fourth generation. It amounts to:
- for users with a high level of mobility (up to 120 km/h) - at least 144 Kbps;
- for users with a low level of mobility (up to 3 km/h) - 384 Kbps;
- for stationary objects - 2048 Kbps.
4G data transfer speeds are:
- the 4G LTE standard boasts a data transfer speed of real 60 Mbit/s;
- speeds of 100 Mbit/s should be provided to highly mobile users, such as trains and cars in motion;
- Users with low mobility, such as pedestrians and fixed-line subscribers, should be provided with 1 Gbit/s speed.
When compared in detail, it becomes clear that the fourth generation technology is 10 times or more faster than its predecessor. In addition, 4G has a number of advantages. For example, if the coating or connection is of poor quality, it is automatically replaced with an older one. In the case of 3G, the same thing happens, but there the previous minimum standard is EDGE, the appearance of which clearly does not please subscribers.
Note! The process of changing the standard in the case of a newer one is as smooth as possible, and even downloads or voice data transfers are not interrupted. This is due to the use of the packet transfer method.
It is clear that fourth generation technology works and should function much faster, because it is a newer step in the evolution.