Despite the rapid development of modern technologies, high-quality mobile communications are not available everywhere. That is why subscribers need to know the MTS coverage area.
This concept indicates the territory where SIM card owners are able to receive a high-quality signal and use cellular communications. This area depends on the location of towers and base stations. But users should take into account that the quality of reception is affected by:
- relief of the surrounding area;
- weather (in thunderstorms and squally winds the quality decreases);
- network load;
- the technical condition of the phone and the ability of the phone to support modern technologies, including 4g.
Users should take each of these factors into account, but remember that it is the radio towers that have the main influence on network connectivity.
What it is
The scale of distribution of mobile communications across regions is very large! Let's try to figure out the definition of equipment that gives us the opportunity to use traffic, make calls and write SMS messages?
- It is the core part of any cellular network;
- Towers act as a link between subscriber equipment (for example, telephone) and wireless radio waves (communications, Internet);
- Equipment installed on the ground creates a coverage area - range and power are regulated by antennas.
Look at the map of Megafon base stations - the more of them in one place, the better the connection!
How to determine the location of towers
If you definitely want to see Megafon cell towers on the map, you can download special software - there are several proven high-quality applications on the network. Why are they even needed? Users download them for different purposes:
- Users can evaluate the actual coverage area of the operator;
- You can easily find free wireless network sources;
- To find out whether your operator will work in a certain location;
- In order to understand how stable the tower signal is - are there any failures or irregularities in operation;
- When purchasing wireless routers, you need to know which way to point the antennas to catch the signal;
- Radio amateurs will be able to determine how much interference there is - and whether there is any at all;
- Often, data is used when choosing housing - after all, everyone needs high-speed and constant access to the network, as well as a stable signal for communication;
- The information is also used during rescue operations - in some corners there are no towers, it is necessary to install special equipment to catch the signal.
Now you understand why users can search for Megafon cell towers on the map. Let's move on to the list of applications - they are all available in the Ep Store or Google Play Market, they can be downloaded for free or shareware.
- OpenSignal;
- Cellulailer;
- Cellumap;
- Network Signal Info;
- Connection quality;
- Cell Coverage Map;
- netmonitor;
- Network Cell Info.
Let's try to search for the nearest Megafon tower in the OpenSignal application:
- Download the program and open it, make sure you are connected to the Internet;
- The interactive coverage will load automatically;
- You will see markings by zones - the colors correspond to the quality level;
- Click on the nearest tower of any operator, marked with a special icon;
- Detailed speed and quality data will open.
Together we looked for Megafon base stations on the map, figured out equipment identification and learned to find signal sources through a mobile application. Agree, it’s interesting to know how our gadgets work, where does the connection come from?
MegaFon Internet coverage area
The Megafon company has its own regional section of the corporate website for each region of Russia. This is where you need to look for coverage areas in a particular city.
To do this, you should first make sure that you have the right section of the site open. It is selected in the upper right corner. Then you need to go to the “Support” menu item and select the “Call shops and coverage map” sub-item there.
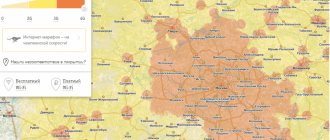
In the Coverage Map section (located on the right), you will see tools for filtering and searching at the top, and below them an image of the most desired territory. Searching by street or metro station is relevant only for large cities, but for rural areas it will be enough to enter the name of the locality. In addition, you can move it with the mouse, zoom in/out to view it in more detail.
There are four checkmarks above the map; these are image layers associated with Megafon services. Main. If you check this box, the map will show the coverage area of regular voice communications. Here, the areas where the service is available are shown in solid green, and the shaded areas are areas where the connection is not available. There are many such places - Russia is very large, we have enough completely deserted territories and there is simply no need to install cell towers there.
3G coverage
If you turn on the “Internet 3G” checkbox, a second map layer will appear. 3G Internet is a newer data transmission technology, and the coverage area of this service is displayed on the map in bright green. As you can see in the screenshot, in rural areas these are only isolated areas, although in large cities 3G works almost everywhere.
4G coverage
Well, the last two layers are the Internet of the 4G+ generation with speeds of 150 and 300 megabits per second. They are displayed on the map in lilac. These services are not available everywhere.
In general, it’s worth saying that Megafon’s accessibility in Russia is already very good; you’re unlikely to find a place from where you can’t at least just make a call. Not all is well with the penetration of high-speed Internet, and this is due to the enormous size of our country.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=RwNsl7edg2E
Generations of base stations and their coverage radius
Each operator has a wide network of 3G (third generation) and 4G LTE (fourth generation) base stations. If you have not yet decided on the choice of operator or want to switch to another, you may be interested in the map of cellular base stations of the operator you need, which will show in detail the coverage area. The range of one station depends on the location and frequency range. 3G stations in megacities reach 500m, in open areas - up to 35km. 4G LTE stations - the radius can be different, optimally it is about 5 km, but if necessary it can be up to 30 km or even 100 km (if the antenna is raised sufficiently).
Mobile operators have learned to combine low and high frequencies. For areas where a small number of subscribers live, but they occupy a large area, networks operating in low bands are ideal. And in large and densely populated cities, high-band networks are being built. Dual-band LTE networks are the future of mobile communications.
How does a base station work?
- The first thing that catches your eye is the transceiver antennas. They are placed on the roofs and walls of buildings, on pipes, and can be on special structures, lanterns, and even on exotic structures (in Egypt, they are disguised as palm trees).
- Radio relay stations in the form of dishes for connecting a base station to a telecom operator's network via radio relay communications.
- Base stations of the 4th and 5th generations - high-speed fiber-optic communication channels are connected to them.
- Related equipment - climate control systems, power supply, ventilation, security, cellular amplifiers, etc. in the building itself or nearby, in special containers or enclosures.
There is an opinion that if there are many antennas, and they are high, and the transmitter works “to its fullest,” then the connection will be better, but this is not so.
The coverage area of some base stations is often deliberately reduced. Various types of base stations are used:
- macro cells with a range of up to 100 km.,
- microcells with a radius of up to 5 km.,
- picocells or femtocells, which are installed in areas with high population density (shaped like a laptop).
Base station communication:
- Small base stations transmit signals to each other via a fiber optic cable system.
- Large base stations that cover long distances communicate with each other through radio relay dishes.
Roskomnadzor reported that the Big Four operators continue to increase the number of base stations in Russia. In the first half of 2021, there were already 624,800 base stations of all mobile operators, which is 9% more than in the first half of 2021.
Megafon has the most base stations in Russia, more than 209,573 of them. In the first half of 2021 alone, 13,005 stations were installed. MTS takes second place - 161,607 (plus 9,654 BS for 6 months of 2018). Beeline is in third place - 130,841 BS (plus 20,625 stations for 6 months of 2021). And in fourth place is Tele2, they have 122,823 base stations (plus 6,868 stations for 6 months of 2021). The construction of base stations is a complex and labor-intensive process, which includes:
- Selection of a site and conclusion of a lease agreement.
- Design and survey work.
- Registration of permitting documentation, sanitary and epidemiological conclusion on the safety of the station for others, documentation for equipment, for metal structures.
- Production of antenna support structures.
- Construction of the foundation.
- Installation of metal structures of masts.
- Manufacturing and installation of equipment containers.
- Installation of antenna-feeder devices.
- Installation of base station equipment and electronic control unit.
- Power supply connection and commissioning.
Feederless base stations have recently begun to be used. They reduce the cost of equipment and its installation; they are used for communications in 3G format.
Base stations are often installed on the roofs of residential buildings. This is permitted by law, but certain rules must be followed:
- The electromagnetic field level (EMF) in the adjacent area should not exceed 10 mW/cm2;
- the antenna should be erected at a level of 1.5 to 5 meters from the roof surface and at a distance of 10–25 meters from other buildings;
- The ability of people to access the roof should be limited.
- The placement of a base station occurs after a meeting of the owners of the premises (in accordance with Article 44 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation), and at least 1/2 of the residents must vote.
Many people believe that cellular operators are raking in billions without investing their funds, but this is not so.
Operators invest money in the construction of cell towers and the installation of base stations. They spend money on a license for frequencies (2G is more expensive than 4G), on rent, maintenance and maintenance of the BS.
Unusual.
- African operators are installing cellular base stations in rivers on special rafts. This increases the coverage area of nearby villages and the river itself. Due to the lack of roads, all main transport routes are by water. It also reduces the likelihood of equipment theft.
- Base station in the Lefortovo tunnel in Moscow. Antennas are slotted radiating cables.
- Base station powered by solar energy in the Krasnodar region and Western Australia.
- In the UK, in the center of Aberdeenshire Forest, an autonomous base station with a power source based on hydrogen fuel cells has been installed. The same station is installed in Scotland, near the ski center.
Where should the external antenna of a cellular signal booster system point?
When installing a cellular booster system, a directional external antenna provides the greatest effectiveness, and it is very important to choose its direction correctly. It should look at the nearest base station of the cellular operator whose signal needs to be strengthened - MTS, Beeline, Megafon or TELE2.
But what to do if you need to strengthen the signal of more than one operator? Of course, it is not always the case that several operators “fail” at once, but such situations still happen. So what to do in this case?
Fortunately, very often several mobile operators broadcast from one tower at once, and then the task is simplified. We simply point the antenna towards such a “multi-operator” base station. What if there is no such tower and the operators you need are located at different base stations? - There are several options:
- If the separation of the base stations of the cellular operators you need is not too great, simply point the antenna in the middle between them (take into account the viewing angle of the antenna).
- If the desired base stations are located far from each other, at a distance greater than the viewing angle of the directional antenna, then the best option would be to use an omnidirectional antenna with a horizontal viewing angle of 360 degrees.
- An alternative could be to use two cellular signal amplifiers and two directional antennas, so that each set faces the desired cell towers, but, in our opinion, this unreasonably increases the cost of the system and this method should be used only as a last resort, if other options fail positive result.
We have decided where the antenna should point, and now we come to the next and most important question...