Modern life is unthinkable without access to the Internet. It accompanies us at work and at home, providing almost limitless opportunities for business development, education and entertainment. And how annoying it is if, while watching your favorite TV series or downloading high-resolution photos, everything starts to slow down.
To ensure that interaction with the World Wide Web does not cause irritation, it is important to choose the right tariff for Internet access, which, on the one hand, should correspond to the tasks set, and on the other, not waste your money.
Let's try to figure out what Internet speed is needed to have fun and not overpay.
Satellite Internet
The most rare, but promising connection option. Now it is used mainly by business representatives and residents in rural areas where there are no alternative connection options.
A set of equipment may include several devices. Included with this:
- satellite dish,
- transmitting and receiving device
- satellite modem.
The approximate cost of equipment for satellite Internet starts from 9990 rubles (Tricolor, on promotion), and access fees: from 1300 to 5000-6000 or more rubles per month.
However, competition in the satellite Internet market is constantly increasing, which naturally leads to lower prices. Breakthrough technologies and cheap satellite Internet are promised to the entire planet by Elon Musk - on May 24, 2021, his company SpaceX has already launched 60 low-orbit satellites, the number of which is planned to be increased to 11,943.
The signal from all these satellites will be transmitted with minimal delay to compact ground terminals (no larger than a laptop), and then sent to client devices: PCs, laptops, smartphones, etc.
Elon Musk promises record low prices and high speed of information transfer - the company’s ambitious plan to capture the global market applies to 50% of Internet users on the planet. All that remains is to wait for the full deployment of the network called Starlink and enjoy the Internet from space.
Wired or mobile Internet?
However, let’s return from the “star” perspectives to the existing reality. If you live in an ordinary metropolis or near regional centers, then satellite Internet will be an unreasonably expensive choice compared to wired and mobile Internet.
When choosing between these two options, you can immediately say that it is better to use wired Internet - connecting to the provider via cable. This choice provides greater protection from external (for example, weather) conditions and can provide higher connection speeds.
There are several types of wired connections, the main ones being twisted pair and fiber optic network cable.
Type #1 - twisted pair
A twisted pair is one or more pairs of insulated, twisted wires covered with a plastic sheath. Due to its low cost and ease of installation, it is the most common type for laying wire (cable) networks.
Type #2 - fiber optic network cable
Today, there is no faster technology than optical fiber. It has no limit on the length of channels, which means it can connect objects that are very far from each other. Through fiber optic cables laid along the bottom of oceans and seas, high-speed Internet connects not only cities, but also continents.
There are many advantages of fiber optic cable that specialists will appreciate more (durability, speed of detection of unauthorized access, high level of protection against interference, and so on). For the average user, the most important advantage of this connection option is the high speed of information transfer.
So, let's draw the line - both options can be used for connection, but fiber optic cable has more advantages (although it is less common).
How much to “hang” in bits?
Each Internet session is accompanied by sending and receiving information, the volume of which is measured in bits and bytes. These are completely different units of measurement that are not equal to each other: 1 byte = 8 bits.
Large volumes are usually measured in the following units:
- kilobytes(KB) = 1000 bytes and kilobits(KB) = 1000 bits;
- megabytes(MB) = 1000 kilobytes and megabits(MB) = 1000 kilobits;
- in gigabytes (GB) = 1000 megabytes.
If you are interested in understanding in more detail the units of speed and the subtleties that affect it, this article will help you.
At the current stage, providers offer tariffs for megabits per second (MB/s), and occasionally you can find offers operating in gigabytes (GB/s).
Providers generally offer a choice of several packages for Internet connection, which differ in speed and price. The price, as a rule, is for monthly Internet use without restrictions on downloading or data transfer for this period. If you think that the price for the service is high for you, choose a more economical tariff. But you must decide for yourself that the speed provided will be enough for you.
Here is an example of current offers for connecting home Internet from well-known operators (Beeline and MTS):
They operate at speeds from 30 to 500 Mbit/s, and the price ranges from 350 to 999 rubles. And these are only 5 tariffs from two operators. There is a much wider range of offers on the market.
How many megabits does the average user need? If you calculate with a reserve, then the recommended connection speed is in the following ranges:
| Type of activity on the network | Recommended speed (Mbps) |
| Browse the network with ads turned off, without downloading photos or watching videos | 0.5 — 2 |
| Comfortable browsing, mail, social networks, music streaming | 2 — 3 |
| Video calls and video conferencing via Skype | 2 — 3 |
| Uploading photos and videos | 10 — 12 |
| Watching videos in HD quality | 8 — 20 |
| Watching videos in 4K quality | 30 — 50 |
| Online games (simple) | 10 — 30 |
| Online games (advanced) | 50 – 250 and above |
All the above values are approximate, but they can help you determine your basic needs and choose the right tariff for you.
When connecting by cable, it is difficult to find a provider or operator that offers packages with speeds of less than 10-15 Mbit/s, which is already quite enough for viewing various sites, videos and slow downloading of large files. For normal surfing the Internet, viewing photos and videos, ultra-high speeds are not required. This means you can save money.
If you are an advanced gamer or your activity involves sending large amounts of information, high-speed tariffs will give you more pleasure from the game and comfort while working.
Some operators have already assessed the difficulties their customers experience when choosing tariffs, and describe the functionality of their packages in more detail:
What else is important to pay attention to?
In the vast majority of cases, the connection speed stated in the tariff may differ from the actual one - when concluding an agreement, it indicates an obligation to provide speeds of up to 200 Mbit/s. That is, there is not a word about the minimum speed.
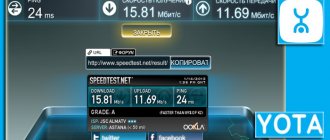
To avoid making a mistake with your choice, you can study reviews of providers, and if you have already connected and have any doubts, you can easily check the speed using a variety of tools. For example, ours.
In our case, when speeds of up to 100 Mbit/s were promised, the actual incoming speed was 71, and the outgoing speed was 98 Mbit/s, which is quite close to the declared one.
If your testing shows serious discrepancies, file a claim with the provider. There is a high probability that specialists will be able to detect and fix the problem. If they don’t respond to your request, just change your provider.
How much does the distance between the router and the device affect?
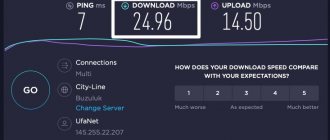
You can determine the dependence of speed on distance using the special SpeedTest service. Naturally, you can use an analogue, but this service best allows you to measure throughput and understand what's what.
With a tariff plan of 130 Mbit/s, the following figures are obtained. On the 5 GHz band:
- 99 Mbps in the room – at a distance from the router in line of sight conditions of up to 5 meters.
- 67 Mbps in the kitchen - through the wall, with a distance of 12-15 meters.
- 5 Mbps in the loggia - with the door closed through a reinforced load-bearing wall at a distance of 12-15 meters.
Few? Here's what the router outputs at 2.4 GHz under the same conditions:
- 36 Mbps – in the room.
- 10 Mbps – in the kitchen.
- 3 Mbps – in the loggia.
From the above test it is clear that devices on 2.4 GHz (this is Wi-Fi 4) receive less speed capabilities than on 5 GHz (this is Wi-Fi 5).
Mobile Internet
We figured out the speed of the wired Internet. The situation with mobile Internet is similar: there are many tariffs and prices, as well as connection options.
In Russia, operators operate in 2G, 3G and 4G-LTE networks. At the same time, Internet prices are significantly higher than the cost of wired Internet. In addition, there are a number of restrictions on the speed of downloading information.
Basically, the price of mobile Internet depends on the volume of information downloaded and network configuration:
2G (second generation, GPRS)
This is the slowest mobile data transfer technology, developed in the 90s of the last century. It is suitable for sending text messages using phone applications such as WhatsApp, ICQ. Data transfer speeds in GPRS range from 55 to 115 kbit/sec.
3G (third generation)
Faster data transmission technology, the most common today. Suitable for transmitting video calls, downloading various content, movies, music, games, viewing Google maps, YouTube, television channels, downloading large files, communicating with friends via Skype, working with remote control programs (TeamViewer), etc. Speed up to 2 Mbit /sec.
4G – LTE (Long-Term Evolution, fourth generation)
Allows data transfer at speeds of up to 100 Mbit/s. This type of communication appeared at the beginning of 2010 and allows you to do everything that 3G does, but at a higher speed. You can watch 2-3 videos, surf several social networks, communicate in instant messengers - and all this at the same time.
The upcoming introduction of 5G networks promises us to completely forget about the nuances of the current tariff system - the innovation will allow us to instantly transfer huge amounts of information. However, this will still have to wait - the introduction of 5G in Russia is expected no earlier than 2021.
Thus, the speed of your Internet connection will primarily depend on the age of your phone or smartphone. Almost all modern devices support the 3G standard, and the number of models with 4G is constantly growing.
Connecting system components
The assembled system
In the photograph of the finished device with the housing cover removed, you can see the following elements:
- Push button.
- E-ink display.
- Raspberry Pi Zero.
- Relay module.
- RGB LED and resistors (their composition depends on the LED used).
- Switch.
- DC/DC converter.
- Female connector.
Component Connection Diagram
The previous figure shows that the positive cable from the power supply goes through the switch to the DC-DC converter (this converts the 12V needed to power the modem into 5V for the Raspberry Pi). Then, through a relay (via a normally closed contact), the power goes to the Female output connector. As a result, it turns out that power is supplied to the modem even if the monitoring system is turned off.
The measurement process can be initiated manually by pressing the button mounted on the front panel. The RGB LED is used to inform the user what exactly the device is doing.
The diagram does not show connecting the display to the Raspberry Pi. The display connection details are shown in the following figure.
Connecting an e-ink display to the Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi GPIO pins
Minimum mobile internet speed
Just like when choosing a speed for wired Internet, choosing a tariff for a smartphone depends on what you plan to do on the network.
For example, YouTube recommends a speed of at least 8-10 Mbit/s for comfortable, smooth viewing of videos in FullHD format, for 4K – from 53 to 68 Mbit/s, and Netflix – from 5 Mbit/s for watching films and TV series in HD and from 25Mbit/s for Ultra HD.
Mobile Internet packages
The next step when choosing the optimal tariff is to determine the approximate volume of information downloaded per month. It is quite difficult to do this by calculation - 1 minute of watching videos on YouTube can absorb up to 75 Mbit, and series on Netflix - from 38 to 188 Mbit.
Therefore, the only recommendation here would be to conduct your own experiment: connect the minimum tariff, and then increase it as needed. If online videos, games and social networks accompany you throughout the day, and your budget allows, you can immediately connect to an unlimited tariff and not think about calculations.
Summarizing the considered connection options and tariffs, it is important to note that user appetites are growing day by day: if yesterday we only communicated on social networks and sent simple files, today we already want to watch online videos (preferably in 4K format), conduct video conferences and play advanced games. Currently, this requires either a wired connection at a speed of 70-80 Mbit/s and higher, or an unlimited mobile tariff connection over a 4G network.
However, tomorrow new video broadcast formats may appear, more capacious than FullHD and 4K. Let's hope that the developments of Elon Musk and his colleagues will also not lag behind. And in the very near future we will completely forget about choosing tariffs and speeds - the Internet will be as accessible as a cup of morning coffee.
Weak processor
The processor, to a lesser extent than the above devices, can negatively affect the speed of Internet delivery. However, it is the “heart” of the computer, and will to some extent determine how quickly data can be written to or read from the hard drive. So, if we are talking about purchasing a high-speed tariff plan, the weak computer processor will need to be replaced with a more powerful one. And these are quite significant financial costs, especially if the processor has to be changed along with the motherboard. If the laptop does not support replacing the processor, you will need to sell it and buy a new one with more powerful hardware.