Hi all! RSSI is a statistical indicator that displays the power level of the signal received by a modem or mobile device. The parameter is used primarily in the field of telecommunications technologies to carry out superficial diagnostics when problems arise with the network or speed. And, although the RSSI indicator helps to assess the quality of the signal provided by the operator, you cannot rely on the obtained figures - without taking into account errors.
The load on the network, the quality of the receiving party’s equipment, the weather – it’s hard to even imagine a complete list of external factors. But we must not forget about internal “irritants”. Mobile operators have even introduced a special SINR (Signal Interference and Nose Ratio) scale, capable of assessing the ratio of the useful signal to the noise received from the source. This is measured in dB and often helps technicians configure routers and routers correctly or connect additional antennas if interference persists.
Tips for checking the signal level of the Yota modem and repairing it if it doesn’t work
Over the course of its existence, the Russian mobile communications provider and operator Yota has acquired many positive reviews, but despite this, situations sometimes occur when there are problems with signal reception or network connection. You can easily solve the problem of why Yota does not work. When the Internet does not work or the speed begins to drop, you need to check the Yota signal level on the company’s official website and then reboot the device. Next, we'll look at other modem problems and tips for fixing them.
Content
How to influence the signal and point the antenna
Before you start experimenting with network equipment and the received signal, it is important to remember: even a powerful antenna and a properly positioned modem will not help if there are many obstacles on the way to the base station. Trees, roofs of houses, mountains and hills - even barely noticeable objects can scatter the signal. But, if external factors are not a hindrance, then it’s worth trying the following:
- Change of location for receiving equipment. It is better to place modems closer to the window (and not behind an “impenetrable” concrete wall) or on the windowsill.
- “Profile” powerful antennas and Internet signal amplifiers are not a marketing gimmick, but effective ways to improve the quality of reception. When choosing, you will have to rely on compatibility with existing equipment and the characteristics specified by the manufacturer. You can make an antenna yourself - see the instructions here.
- It is advisable to avoid sources of interference and noise. According to the tests, even external hard drives can disrupt the connection and lead to unexpected results - a drop in speed and deterioration in network access.
- The same MDMA tool will help you choose a suitable location for the modem. The main thing is to update statistics through the interface more often.
Tips for increasing speed
Sometimes there are situations where the data transfer speed is low. If the Internet speed has dropped, you need to fix the device where the signal level reaches its maximum. The place where the Internet speed is high is considered a window. To fix the device in the right place, you need to purchase a USB extension cable. After completing the installation, you need to reboot the modem.
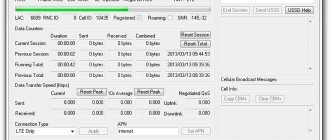
LTE signal quality parameters
To determine the signal quality, pay attention to the “Signal (CINR / RSSI)” value. Using these values, you can evaluate the quality of the 4G LTE signal.
CINR (Carrier to Interference + Noise Ratio) also called SINR (Signal to Interference + Noise Ratio) is the ratio of the level of the useful signal to the noise level (or simply the signal-to-noise ratio). The CINR value is measured in dB.
A positive CINR value means there is more useful signal than noise. The minimum value acceptable for stable network operation: CINR = 10 dB.
NOTE: Important! The higher the CINR value, the better the signal quality.
A negative CINR value will mean that there is more noise in the received signal than there is useful signal. With negative or close to zero values, an LTE connection cannot be established or it will be extremely low in speed and quality.
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) - indicator of the strength level of the signal received by the modem. The value is measured in dBm. The minimum value acceptable for network operation: RSSI = -85 dBm.
NOTE: Important! The higher the RSSI number, or the less negative it is, the stronger the signal strength (for example, a value of -48 is greater than -78). RSSI indicates the strength of the signal received by the modem, not the strength of the Base Station signal.
Below are the approximate values of the CINR / RSSI parameters and their evaluation.
TIP: Note: These values are not absolute. Determining exact values in this case is impossible, because The quality of the LTE connection depends not only on the indicators under consideration, but also on a number of other factors (on the workload of the Base Station, on the quality of the equipment at the BS, on the weather, etc.). The evaluation of parameters is conditional (subjective) in nature and is based on our practical experience and data received from users. The CINR and RSSI parameters are not directly related to each other, i.e. There may be cases when one of the values will be high and the other extremely low.
Excellent performance: CINR from 30 and above / RSSI to -65 Good performance: CINR from 20 to 30 / RSSI from -65 to -75 Satisfactory performance: CINR from 10 to 20 / RSSI from -75 to -85 Poor performance: CINR from 10 or less / RSSI from -85 or less
NOTE: Important! For some modem models, signal quality parameters may not be displayed. The output of this information depends on the type of modem and its capabilities. This feature is not available for some modems. Signal quality parameters are displayed only if the modem itself transmits them to Keenetic. Typically, information about the signal level is transmitted by NDIS or CdcEthernet class modems, not RAS. If you do not see the values of the signal parameters in the Keenetic web configurator, look at them in the USB modem’s own interface.
Starting with the release of KeeneticOS 3.4.1, the web configurator has added a display of signal strength and 4G/3G network type for USB modems.
Two conditions that are important when choosing a cellular amplifier
To select the optimal set of equipment for a dacha, apartment or office, you need to determine:
- Signal strength coming from the base station
- Its frequency range and communication standard: GSM, UMTS, LTE
When talking about the strength of a mobile phone signal, many people think that its level can be assessed by the number of “bars” on the mobile phone. This is one of the easiest ways to do this, but unfortunately not the most reliable.
Most phones have an "Engineering Menu Mode" option. It allows you to more accurately find out useful information using your phone, including the signal strength in decibels and the 3G/4G or GSM frequency band that the telecom operator uses in your area. Knowing these parameters is extremely important for choosing the right amplifier model.
Lost signal
Subscribers complain about unstable reception and that the speed may suddenly drop or the signal may be lost. As a result, Yota’s Internet does not work well or is constantly disconnected. If this does not happen often, then you need to move the operating device to another place where you can see a stable signal. If the malfunction begins to appear regularly and Yota works slowly for several days, then everyone connected to the network can contact the technical service, they will tell you in more detail how to solve this problem.
SINR and RSRP - what are they?
The received signal on a mobile router or modem can be characterized by several basic parameters. Let's look at them briefly. This will help you correctly install and configure the antenna to receive a high-quality mobile Internet signal, and as a result, get a stable connection to high-speed Internet.
Here's what the Yota 4G (LTE) modem monitoring panel tells us about the signal quality:
Signal quality (SINR/RSRP): 12 dB / -80 dBm
RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power) - the average value of the power of received pilot signals (Reference Signal) from the Base Station of the cellular network. Roughly speaking, this is the absolute level of the transmitter signal from the cellular station as the modem hears it. The RSRP value is measured in dBm. With RSRP values = -120 dBm and below, the LTE connection may be unstable or not be established at all.
SINR (Signal Interference Noise Ratio) - signal-to-noise ratio in the receiving channel. If the value of this parameter is 0 dB, the signal level is equal to the noise level, if positive, the signal is higher than the noise; with a negative value, the signal is below noise (even in such a situation, the modem can receive something, it’s just that the reception quality will be poor, there will be a lot of errors).
These two parameters speak about significantly different things. The modem can hear the cellular station well, RSRP is high - but the level of noise interference at the receiving point will be such that the SINR is close to zero and the connection is barely warm. And vice versa - the signal may not be very loud, but there is little interference, and reception is normal.
In general, in urban environments where there is a lot of interference, the SINR parameter is more important than RSRP. You should try to tune out interference even at the cost of some reduction in the audibility of the station. But outside the zone of reliable reception, somewhere outside the city, where there is little interference, maximizing RSRP can come to the fore.
So, what values of these parameters should you focus on:
SINR > 20 is an ideal signal; this almost never happens. SINR from 0 to 13 is satisfactory. The bigger, the better. SINR
This material was independently published in our community by the user proper on the basis of the current version of the User Agreement. If you believe that such a publication violates your copyright and/or related rights, you must notify the site administration by EMAIL indicating the address (URL) of the page containing the controversial material. The violation will be eliminated as soon as possible, and the perpetrators will be punished.
Driver won't install
Newly connected subscribers encounter this problem. If the driver cannot be installed, you must change the security settings responsible for their installation, and then be sure to restart the computer.
Of course, if you use the Internet on your phone, you can avoid the troubles associated with using WI-FI devices. But it's not always possible to get work done via a mobile device. And which option for accessing the Internet to give preference to is determined by each person himself.
Programs for smartphones and tablets on Android
Android programs load and update data faster than the web interface. Therefore, they make it easier and faster to set up an Internet antenna in a private home.
These programs were developed by 4pda.ru enthusiasts and are therefore distributed directly and not through the Play Market. To install them, you need to temporarily allow the installation of programs from unknown sources: “Settings / Lock screen and security / Unknown sources” set the switch to ONCE.
The programs can be downloaded here:
- For Android 5 here
- For Android 6.0.1 and below (up to 4.1.2) download the apk file here.
To use these programs:
- Install the program on your phone or tablet.
- Insert the modem into the router and connect to the router via Wi-Fi.
- Launch the program and click the Connect button.
- If everything is done correctly, you will see the signal level on the screen.
For these programs to work, the following conditions must be met:
- The Huawei E3372 or E8372 modem must operate in Hi-Link mode.
- The modem must have firmware that displays the signal level.
- The modem must have a web interface compatible with the programs.
- The modem must be accessible at 192.168.8.1
How to find out signal strength on Android. Method number 1.
In the application you can see at what frequency, what technology (2/3/4g) the operator is working on and what the signal level is.
The screenshot shows that MTS operates in 3G (HSPA+) at a frequency of 900 MHz, signal level -75 dB, velcom operates in 4G (LTE) at a frequency of 1800 MHz, signal level -106 dB.
How to find out signal strength on Android. Method number 2.
If it is not possible to download the application, then you can determine the signal level and network type using standard Android system tools. This method has a significant drawback - the frequency at which the signal is received from the telecom operator will remain unknown.
How to find out signal strength on iPhone
Now, based on the ARFCN value, you can determine the frequency range from the following table:
| Standard name | Frequency ranges | Icon on the phone | Possible designations of operating ranges in phones and programs | Range of values for ARFCN, UARFCN or EARFCN |
| GSM-900 (2G) | 900 MHz (Band | E, G, no icon | GSM900, EGSM900, Band 8 | 0.. 124 |
| GSM-1800 (2G) | 1800 MHz (Band 3) | E, G, no icon | GSM1800, DCS, DCS1800, Band 3, Band 4 | 512.. 885 |
| UMTS-900 (3G) | 900 MHz (Band | 3G, H, H+ | UMTS900, Band 8, Band 1 | 2712.. 2937 |
| UMTS-2100 (3G) | 2100 MHz (Band 1) | 3G, H, H+ | Band 1, UMTS2100, WCDMA2100 | 10562.. 10838 |
| LTE-800 (4G, LTE) | 800 MHz (Band 20) | 4G, LTE | 800MHz, Band 20 | 6150.. 6449 |
| LTE-1800 (4G, LTE) | 1800 MHz (Band 3) | 4G, LTE | LTE1800, DCS, DCS1800, Band 3, Band 4 | 1200.. 1949 |
| LTE2600 FDD (4G, LTE) | 2600 MHz (Band 7) | 4G, LTE | LTE2600, Band 7 | 2750.. 3449 |
| LTE2600 TDD (4G, LTE)** | 2600 MHz (Band 38) | 4G, LTE | Band 38 | 37750.. 38249 |
Additional customization features
Before you start setting up your modem, you need to update it. How easy or difficult it is to update the firmware depends entirely on the manufacturer and model of the device.
In most modern modems, firmware updates are available through the standard administration interface, so just click the firmware update button. Older models require visiting the manufacturer's website, downloading the firmware file from the device's support page, and uploading it into the administration interface. It's worth updating the firmware regularly for improved performance, improved features, and security updates.
Most modern modems now come with Quality of Service (QoS) tools to limit the amount of bandwidth used by applications. You can use QoS to prioritize different applications at different times of the day. QoS settings are located in the advanced settings in the network administrator interface.
Where is RSSI
RSSI begins its work in the control equipment receiver, but not every receiver has this feature.
The receiver is what is placed in the quadcopter and receives the signal from the control panel.
RSSI can be connected to the receiver output of the flight controller or OSD. Some receivers do not have a special pin for this function and you have to come up with ways to work around this problem. If your control equipment can receive telemetry, it can most likely receive RSSI data.
For example, FrSky Taranis equipment with a D4R-II receiver has RSSI. RSSI pin connects to OSD to display data in FPV helmet or goggles.
If there is no OSD, then you can set up an RSSI alarm about a weak radio signal on the remote control beeper. Such a signal will allow you to fly more calmly, and if the signal is weak, the remote control will notify you of this with a sound signal. This will be even more convenient; you don’t need to monitor the values on the screen and be distracted by it.
Settings for 4G network
For fourth generation networks, the characteristics already discussed will be displayed:
- CIRN (Calcific Information to Noise Ratio). When the value is around 0, the connection speed and connection quality are low. A low value indicates a lot of noise and a weak signal.
- RSSI, signal strength at the receiving point. Good communication quality will be at values from -80 dBm to -58 dBm.
- Band. Base station operating frequency.
For each type of network, a frequency pool is allocated:
- 2G: 900 to 1800 MHz;
- 3G: 900 to 2100 MHz;
- 4G/LTE – frequencies 800/900/1800/2600 are used.
The program will also offer additional applications for Android that you can download and use.
Why is dBm negative?
Power, expressed in dBm, is the decimal logarithm of the ratio of received power to 1 mW. (Recall that 10 to the power of -3 is equal to 0.001, that is, -3 dBm = 0.001 mW). Since a cell phone remains a fairly low-power but sensitive device, its parameters are characterized by a negative number.
Remembering that -80 is less than -40 is very simple: use the association with a bank account. If the account has -80 thousand, then you actually have less money than if the debt was -40 thousand.
How to choose a 2G/GSM and 3G/4G Internet signal booster for your dacha
This article explains in simple and accessible language what a cellular signal amplifier is, what types of amplifiers there are, what is their difference, and gives some tips on choosing and installing these devices. More examples of photographs of completed work can be found on the Instagram account @mobilebooster.ru.
There are two main types of cell phone boosters:
- router (modem) + external antenna;
- repeater with a set of antennas.
Outdoor antenna with indoor router
This option perfectly enhances the 3G/4G Internet, but does not enhance regular voice communications. Voice communication can be used through applications such as WhatsApp, Skype and others.
The connection diagram is simple: the antenna is on the street (ideally on the roof), and the router itself is located indoors, where it distributes the Internet signal via a Wi-Fi network.
Some important points when choosing an antenna
Let's consider the key points when choosing an antenna, since the final speed of the Internet depends on this. That is, if you choose and install the antenna correctly, you can get speeds 3-4 times faster. And this is not an exaggeration! So…
Antenna with a router or modem inside. There is a popular option for antennas in which the modem or router itself is hidden inside the device. And it is no longer a tight coaxial cable that enters the room, but a soft twisted pair cable.
It is strictly forbidden to take them, because the modem and router intended for indoor use operate at temperatures from 0 to +40 degrees according to the passport! At the same time, in winter, the router can heat itself in a confined space, if you do not have to do a cold start at -20 degrees, at which a breakdown often occurs. And in the summer, in the sun, the temperature inside the antenna housing can reach up to +80 degrees. In most cases, such solutions last no more than one and a half years. Be careful: sellers of such antennas constantly convince that everything will work perfectly. Moreover, they assemble such devices almost on site in the trade pavilion.
Don't go for high gain antennas. Firstly, in practice there are no more than 17 dB, even if it is large and the piece of paper that comes with it (in the passport) says 27 dB! In practice, the maximum was 16-18 dB. This is practically the limit in the segment costing up to 10 thousand rubles. Secondly, the higher the (KU), the narrower the radiation pattern and the more difficult it is to accurately point the antenna at the base station of the cellular operator.
An example of an antenna pattern with gain = 16 dB:
That is, the maximum gain according to the passport is achieved only when the antenna is precisely directed towards the base station of the cellular operator. As you can see from the diagram, with a deviation of approximately 25 degrees, the actual gain will be only 2 dB (highlighted in red)! And for antennas with a higher gain, a deviation of 2-3 degrees has a colossal reduction in the actual signal gain!
Another important point: in practice, if there is no direct visibility to the base station of a cellular operator (neighboring buildings, forest, terrain), then an antenna with a wider radiation pattern (lower gain) picks up the Internet signal better. This is noticeable not by the signal level, but by the Internet speed! This is due to the RSRQ and SINR parameters.
What does dBm ASU signal level mean?
One of the designations for the ratio of the level of transmitted information to noise in the pilot channel is denoted as ASU. The pilot signal is radiation that is continuously (background) transmitted by the Base Station. The power level remains constant, it is always 4-5 dB higher than in the information channels.
The ASU parameter is displayed not in decibels, but in points. The table for converting points to dB looks like this:
- 0-1 ASU: RSSI level is less than -110 dBm, the signal is weak, unstable, interruptions are possible;
- 2-3 ASU: RSSI value from -110 dBm to -105 dBm, signal on the verge of shutdown, very weak;
- 4-5 ASU: RSSI value from -95 dBm to -105 dBm, is in the “uncertain reception zone”;
- 6-7 ASU means good signal quality on the street or in transport.
If the ASU indicator is higher (13 or more), then the RSSI value is greater than -75 dBm, which guarantees high quality communications in buildings, premises, and areas with variable terrain.
The best achievable value for this parameter will be around -50 dBm. It means that the signal is clear, stable and clearly distinguishable.
How to find out what frequency a cellular operator operates on
Based on the value of the absolute radio-frequency channel number (ARFCN), you can determine the frequency range from the following table:
| Standard name | Frequency ranges | Icon on the phone | Range designations in phones and programs | Range of ARFCN, ARFCN or EARFCN values |
| GSM-900 (2G) | 900 MHz (Band | E, G, no icon | GSM900, EGSM900, Band 8 | 0 … 124 |
| GSM-1800 (2G) | 1800 MHz (Band 3) | E, G, no icon | GSM1800, DCS, DCS1800, Band 3, Band 4 | 512 … 885 |
| UMTS-900 (3G) | 900 MHz (Band | 3G, H, H+ | UMTS900, Band 8, Band 1 | 2937 … 3088 |
| UMTS-2100 (3G) | 2100 MHz (Band 1) | 3G, H, H+ | Band 1, UMTS2100, WCDMA2100 | 10562 … 10838 |
| LTE-800 (4G, LTE) | 800 MHz (Band 20) | 4G, LTE | 800MHz, Band 20 | 6150 … 6449 |
| LTE-1800 (4G, LTE) | 1800 MHz (Band 3) | 4G, LTE | LTE1800, DCS, DCS1800, Band 3, Band 4 | 1200 … 1949 |
| LTE2600 FDD (4G, LTE) | 2600 MHz (Band 7) | 4G, LTE | LTE2600, Band 7 | 2750 … 3449 |
| LTE2600 TDD (4G, LTE) * | 2600 MHz (Band 38) | 4G, LTE | LTE2600, Band 38 | 37750 … 38249 |
LTE Band 3 (1800 MHz) is the most common band, completely covering the entire Moscow region.
LTE Band 7 (2600 MHz) is used only in large cities, where simultaneous servicing of a large number of subscribers is necessary.
LTE Band 20 (800 MHz). Used in regions in sparsely populated areas with open areas, it is characterized by a large coverage radius and penetrates well into buildings.
LTE Band 31 (450 MHz) is used by Tele2, and the equipment is known under the SkyLink brand. It has the largest coverage radius and is used in remote and sparsely populated areas. It is not supported by smartphones; only modems and routers work with it.
* LTE Band 38 (2600 TDD) is used only in Moscow and the Moscow region by Megafon and MTS operators.
How to check network stability on a mobile device
Modern smartphones and tablets have software that allows you to determine the signal level, its reliability and stability. This feature is best implemented on the Android OS. To determine stability, it is recommended:
- open the list of available applications on the Play Market;
- use the search to select what you need (experts suggest Network Signal Information or similar);
- download the application to your phone and launch it;
- Having entered the interface, select the “Mobile” sub-item;
- The “Signal Strength” window will display the current network status.
Based on the data obtained, you will be able to assess the strength and stability of the signal.