Manually setting up Wellcom Internet on Android takes a few simple steps: Go to Settings, select “More…” > select “Mobile network” > “Access points (APN)” > select “Add”. For Velcom Belarus they will be as follows: Name = “Velcom”, APN = “web.velcom.by” . Settings
- Automatically using the Settings Wizard...
- USSD request *135*0# call
- Personal account (Settings menu item)
- Send an SMS with the word “internet” to number 512. ...
- Configure the device manually
What is an Access Point Name (APN)
APN is the information your phone uses to connect to your carrier's network. It lists the addresses your phone uses to connect to the network, the ports used to process Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) messages, the types of data a particular APN uses, and other pieces of information to ensure your phone works properly.
Some of the settings, such as "APN Type", may be optional and your phone will still work if it is not 100% correct. Others, such as "MMSC" and "APN", are much more important and your phone will not work if they are entered incorrectly.
Luckily, most phones have a built-in APN for popular carriers, so all you have to do is insert your SIM card and let your phone do its magic. The phone already has an APN and it knows which one to load to connect to a given network.
Enabling LTE and 4G networks, manually setting up the Internet: Tele2, MTS, Megafon and Beeline
Nowadays, when purchasing a smartphone, users pay attention to the possibility of supporting new generation networks. After all, the higher the Internet speed, the faster sites will load and media content will be played. A few years ago, a new mobile communication standard, 4G (LTE), was introduced.
With its help, smartphone owners were able to use high-speed Internet. Almost all new devices are equipped with this type of connection, and users are often interested in how to set up 4G on their phone. In this situation, you can use the settings of your mobile operator or enter the parameters manually.
Cellular trends
It’s no secret that today the Internet is emerging, and probably has already taken a leading position among the ways of people’s communication. Today, even the simplest push-button phones, not to mention smartphones and tablet PCs, are almost never produced without the function of accessing the Global Network. The Velcom operator has not remained aloof from modern trends and for more than 10 years has been providing its subscribers not only with voice communications, but also with access to wireless Internet.
The quality of the service is quite high and is positively assessed by new and existing Velcom subscribers. Setting up the Internet in the case of mass access devices is quite simple and should not be difficult even for novice users of phones, smartphones and tablets. Let's talk about this in more detail later.
How to set up your phone
If we are talking about a simple push-button telephone, but with support for Internet access and used in the Velcom network, setting up the Internet does not bring any problems to the owner at all, everything is done automatically in 99% of cases. This approach is provided by a special service called the “Settings Wizard”. To gain access to the Internet, the user just needs to register for the first time in the Velcom network - the Internet will be configured automatically, the phone will receive the necessary data for GPRS/MMS work directly from the cellular network.
If the settings do not arrive automatically, you can use USSD requests - dial the combination *135*0# on your phone keyboard and press the call key. PRIVET prepaid subscribers have a different way here - the combination *126*0# and the same call key. In addition, any subscriber can use Velcom’s Internet subscriber service system. Setting up the Internet using this system is literally two clicks of the mouse on the necessary items.
How to set the necessary settings?
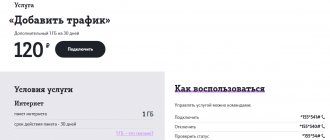
Previously, this process was carried out by sending an SMS request to connect Internet services within a certain tariff. The operator responded by sending the settings, saving which the subscriber received access to the mobile Internet and other services. Over time, operators optimized this process and began to independently send the necessary information for the APN as soon as the SIM card was in the new device.
Despite this service, manual APN configuration is still relevant. The need for it arises when the parameters are lost for some reason or the automatic identification fails. Now I will tell you how to do this yourself, and you will see that it is much easier than remembering the request code or using other methods.
To begin with, I recommend understanding the settings of your smartphone. And find the place where you will enter the data.
- In the most common Android devices, your path in the settings menu will be as follows: “Mobile network” (you may find it in the “More…” section, depending on the software version) – “Access points (APN)”. Next, if you have a dual-SIM model, select an operator. And we see many parameters (we will return to them later).
- On Apple phones, in the settings we find: “Cellular (data)” – “Data settings” – “Cellular data network”. Here you will see concise APN settings for individual services;
- On Windows Phone devices, everything is even simpler: scroll through the numerous settings towards the end of the list, where “Access Point” awaits you.
Select the operator and get to the desired parameter entry menu.
What are the access point settings for?
In most cases, mobile communication services are used using smartphones and phones. These devices must be configured in a certain way to transmit a packet of information.
First of all, these settings are checked by the mobile operator providing this service.
This allows him to determine
- List of IP addresses assigned to this gadget;
- Data protection and encoding tools;
- The procedure for working with additional devices connected to this channel;
Correct IPN settings allow you to install the desired packet data network (PDN) for information exchange. In this case, it is possible to identify and select a specific service:
- communication with the WAP wireless application server;
- MMS multimedia messaging protocol;
- packet radio communications;
- directly Internet;
Two parts
Despite such extensive functionality, the APN structure is quite compact and consists of two parts:
- The first (mandatory) is the network identifier. The name of the connected external network that has a special support node is written here. In addition, the type of service requested by the user may be added to this information.
- The second is the operator identifier. Here the packet domain in which the operator operates is already indicated and the GGSN node responsible for its connection with the Internet Protocol (IP) is located. It is also mandatory to define MCC and MNC codes, which respectively identify the country and operator.
In simple terms, without correctly setting up the APN, working with the Internet via a mobile network is out of the question. How relevant this is is needless to explain, since this topic is the most promising today.
Software and application developers are moving their products to the mobile platform whenever possible. Now the phone is the main intermediary between the network and the user (in games, at work, at home, during financial transactions). For their part, this is actively supported and developed by gadget manufacturers and operators, providing support and distribution of high-speed data transfer standards (LTE and, currently being finalized, 5G).
And of course, we, users, are delighted with the opportunity to access any quality content anywhere in our environment. To do this, you need to correctly configure the APN settings. Those who like to use VPN to access prohibited resources can rest easy. The identifying information you exchange with the operator will not be shared online.
Enabling and setting up 4G (LTE) on Android smartphones
There was a time when wired Internet speed was measured in kilobauds (kilobits per second), and 14,400 baud was considered a good value. Today, wired access operates in hundreds of megabits/second, and this no longer surprises anyone. But the speed of wireless communication is noticeably lagging behind, and the efforts of developers are focused on promoting new high-speed communication standards.
The transition from 2G to 3G could not be called revolutionary, but the progress was obvious. Fourth generation networks have made it possible to bring the standards of mobile Internet access closer to wired technologies. But - with some restrictions. Today we will tell you about them, as well as about ways to connect Android smartphones to the 4G (LTE) standard.
What is an LTE network on an Android phone?
Although the concepts of LTE and 4G are not equivalent in the technical literature, both terms are actively used to refer to fourth generation networks.
In fact, the 4G LTE standard can be considered as an intermediate stage in the evolution from 3G to networks starting with four (full 4G, its extension 4G+ and a half-frequent 4.5G solution, something in between 4/5G). Considering how much data flows circulating over mobile networks have increased, it can be argued that the transition to high-speed networks is overdue and is an urgent need. However, LTE technology is already preparing an even more impressive replacement - 5G networks, the development of which is already at the experimental launch stage.
If we talk about technology in relation to smartphones, then you need to know the following: this is a radio module included in the phone, capable of operating in an extended frequency range (from 1.4 to 20 MHz) with the implementation of the channel differentiation function. In simple terms, 4G LTE provides much more radio bandwidth than 3G. As a result, it became possible to provide higher data transfer rates while improving the quality of cellular communications. Streaming video, IP telephony, video calls - all these things are impossible with mass use in 3G networks, but now they are actively used by both the business sector and ordinary people.
Thus, those 3 MB/sec, which satisfied users for a long time within 3G, have today been replaced by speeds of about 21-75 MB/sec. The difference is obvious. But you need to understand that increased data transfer speed is not the only trump card of 4G LTE. Other advantages of the standard include the following:
- ensuring communication stability - it will remain stable in the zone of reliable reception, even if you move at speeds of about 300 km/h;
- the frequency range of the standard has been significantly expanded;
- transmission of packet data sets is carried out using radio switching.
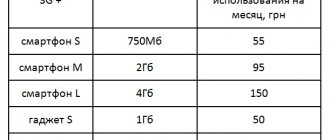
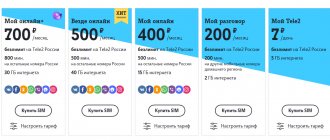
It cannot be said that networks today cover the entire planet - even in South Korea, where this figure is the highest, the coverage level is 96%. In Russia, 50% of the territory is covered by fourth generation networks provided by the so-called “Big Four” domestic mobile operators (MTS, Beeline, MegaFon plus the growing Tele2).
Checking smartphone compatibility with 4G
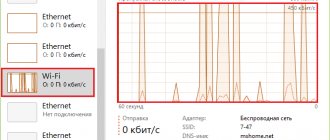
Your mobile device may be capable of high speeds. How do you know if you can enjoy the opportunity to work on 4th generation networks? There are several ways to perform this check.
Checking your smartphone's SIM card
The first limitation to overcome concerns the SIM card itself. If it doesn't support 4G LTE, you'll have to replace it. The method is simple. Just enter a special code and press the call button. The problem is that this code is different for mobile operators. You can find out the appropriate USSD code combination on the official website of the service provider.
So, for Tele2 this combination looks like *156#, for Beeline - *110*181#, for Megafon - *507#. Finally, for MTS it is *156#.
After dialing the code and pressing the call button, you should receive an SMS message informing you whether you can use high-speed access or whether you will have to change your SIM card. Note that LTE networks began to be implemented in Russia in 2012, so if the SIM card was released later, most likely it is in the USIM format, which means you will not be left without 4G.
Verification via phone
The second limitation is related to the phone itself. Old push-button phones obviously lack the ability to receive data at high speeds. But modern smartphones are different. Frankly budget Chinese models may also not support the LTE standard, so this fact must be taken into account when testing the phone. And you can do this in different ways:
- using the same USSD codes as for identifying a SIM card. The possible answer is that the SIM card supports 4G, but the phone does not;
- When purchasing a new smartphone, carefully read the instructions, where all supported networks will be listed in the phone's specifications. If among them there are the designations 4G/LTE/WiMAX, this means that the device supports operation in fourth generation networks. The same data is usually given on the box (packaging);
- If you are one of those users who are not used to cluttering your desktop drawers with phone boxes along with instructions, you will have to use a different method. Go to the “Settings” item of your smartphone, select the “About phone” sub-item and the section describing the status of installed SIM cards, where, among other characteristics, the connection type is indicated. Depending on the Android version and device model, the access path and menu item names may differ, but in principle you understand where to look;
- in extreme cases, no one bothers you to find the necessary information on the Internet - any website that sells smartphones indicates the full technical specifications of each model. Another thing is that you shouldn’t trust such data 100%, so use several sources of information.