Features of MTS virtual PBX
MTS provides virtual PBX services exclusively for corporate clients – new and existing. It is designed for prompt telephone installation of workplaces in enterprises without significant equipment costs. The VATS functionality is performed on the MTS side - forget about expensive office PBX units with modest functionality and often paid installation. Fill out the application on the MTS website, sign the contract and start setting up the equipment at your workplace.
Key features of virtual PBX from MTS operator:
- Flexibility in settings – the management system allows you to set flexible call distribution scenarios, manage employees and call transfers;
- There is a free trial period - its duration is 28 days. During this time, you can fully study the functionality of the PBX and decide whether it is suitable for business needs. It should be noted that MTS offers one of the longest test periods in the office telephony market;
- Several tariff plans - from a simple multi-channel number with a basic set of services to advanced packages with powerful functionality;
- Free communication within the company - communicate with colleagues for free, even if they are in other branches;
- The ability to combine several departments and branches into a single network for more productive business work;
- The ability to organize VIP support for important clients, assigning personal managers to them and directing all requests only to them.
Virtual PBX from MTS improves the quality of customer service and makes the work of enterprises more productive, which can be assessed by monitoring the level of sales and employee efficiency.
Setting up a trunk from MTS.
This article will describe the registration of a trunk from MTS, which is provided as a separate cable to the operator’s closed VLAN network.
- Receiving settings from the operator. Description of the configuration.
- Configuring VLAN for the operator's network.
- Routing to the operator's network.
- Setting up a trunk on FreePBX.
- Configuring the Asterisk SIP Settings module.
- Setting up incoming logic.
- Setting up outgoing logic.
The following settings were received from the telecom operator:
Trunk mode: without registration in point-to-point mode (IP2IP). SIP Server: Signaling - 172.16.253.3, port: 5060 UDP (SIP) Media: 172.16.253.4 (RTP) Codecs: G711a/u DTMF protocol: rfc-2833 network: 172.16.161.96/30 IP address: 172.16.161.98 mask: 255.255.255.252 gateway: 172.16.161.97
So, what we received from the operator: a trunk without registration in point-to-point mode, SIP signaling data, media stream data, codecs used, DTMF protocol, network parameters, client IP, network mask and operator gateway.
The VoIP server is based on CentOS 6.9, there is 1 interface with a local IP, a server behind NAT, and the server also has a second network card.
Connection diagram: the first network card is used to connect the server to the company's LAN. The second network card will be used to connect the server to the operator's network.
Let's move on to setting up the second network card. To do this, log into the server via SSH as root, then use the system-config-network utility. Enter in terminal:
# system-config-network
utility in terminal
We will see the following window:
The utility interface is simple. You can configure DNS settings, or you can configure a new interface.
utility interface A notable feature of this utility is that when configuring a new network card (optional), the MAC address will be assigned automatically.
Because We have a new network card installed, let's go to Device configuration:
Device configuration
A window with existing interfaces will open. In my case, the interface has already been created. It's called eth1–r8169. To create a new interface, select .
Let's create it with the following parameters:
parameters of the second network card
- Specify the interface name
- We duplicate the device name
- Use DHCP – NO
- We indicate the parameters of the static IP address from those provided to us by the operator.
- Specify the mask from the operator.
The DNS and Default Gateway parameters should not be specified, and the Default Gateway parameter cannot be specified, because The system cannot have 2 default gateways.
We save and exit.
Let's enter ifconfig in the terminal to check the status of the interfaces:
# ifconfig
checking the status of interfaces.
The interface does not rise, which means you need to raise it yourself. To do this, let's enter:
# Ifup ifcfg-eth1
raising the network interface.
Let's check again:
# ifconfig
status of network interfaces.
The interface is up. You can move on to routing.
Let's register routes to the provider. To do this, you can go in two ways - create a temporary route, or create a static route that will work when the interfaces start. Let's consider the second option. To do this, create and open a new file along the path:
# nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-eth1
Let's fill it with the following content:
filling the route file. 1. 172.16.161.97 dev eth1 2. 172.16.253.3 via 172.16.161.97 3. 172.16.253.4 via 172.16.161.97
1. gateway for interface eth1
2. routing for SIP (signaling)
3. routing for RTP (media)
Save, exit, then execute a sequence of commands to reboot the interface:
# Ifdown ifcfg-eth1 # Ifup ifcfg-eth1
Checking the routing:
# netstat –rn
route table.
Let's ping the gateway to make sure that we are connected to the operator's network:
#ping 172.16.161.97
ping to the operator's gateway.
The gateway is pinging, you can proceed to setting up a trunk on FreePBX.
Troubleshooting: if the gateway does not ping, you need to check the correctness of the settings provided by the telecom operator, especially routing, check the firewall settings on the PBX, it can act as a blocking link. As a last resort, contact your telecom operator to jointly debug the problem. If you tried to create a config for the interface manually, but it did not work for some reason, do it through the system-config-network utility.
Go to Connectivity – Trunks:
Connectivity – Trunks
Create a new trunk Add SIP Trunk:
creating a new trunk.
Specify the following parameters in the trunk. I remind you that the trunk is ip2ip, without registration:
trunk parameters.
Below are the trunk parameters in written form:
host=172.16.253.3 type=friend qualify=yes port=5060 dtmfmode=rfc2833 nat=yes insecure=invite,port disallow=all directmedia=no context=from-trunk allow=alaw&ulaw
Save the changes, apply, check the peer in Asterisk:
CLI> sip show peers
peer status in Asterisk.
The feast is ready.
In order for the trunk to work correctly, you need to configure the SIP Settings module as follows:
SIP Settings module settings.
- Because our server is behind NAT, then parameter = YES.
- IP Configuration - Static
- External IP – we indicate the IP address of the eth1 network interface, which was provided to us by the operator.
In order to configure the incoming logic, let’s go to Connectivity – Inbound Routes. You can specify a specific DID for call distribution, or you can use the Any DID / Any CID routing principle. In this example, the implementation is via Any DID / Any CID, then the call enters the queue. You can have everything optional.
This point has its own nuances. Let's go to Connectivity – Outbound Routes to configure outgoing routes:
setting up outgoing.
In order for a call to go through in the outgoing direction, you must enter a 10-digit number for outgoing in the CID field, because in another format, MTS will not miss your call.
This is due to the fact that for outgoing calls, the CID is substituted into the From and Contact fields in SDP. If the operator receives data in the wrong format, the call will be disconnected.
Example:
Incorrect: From: ;tag=as4e2b6f8a
Required: From: ;tag=as4e2b6f8a
Incorrect: Contact: sip: [email protected] :5060
Required: Contact: sip: [email protected] :5060
At this stage, the setup is completely completed, enjoy your use.
Virtual PBX capabilities
Let's give a brief instruction on the capabilities of VATS from the ATS company. The most important function is call distribution. The system provides flexible scenarios that allow you to load the call center evenly or create a motivation system, thanks to which each consultant can independently take the initiative and answer the next call faster than others. A flexible call distribution system will ensure high-quality call processing, allowing you to work with each client.
Voice greeting and voice menu are two inseparable functions. The first greets callers, introducing herself on behalf of the company. Next, the voice menu comes into play - it can be single-level or multi-level, depending on the needs of the business. Multi-level menus often contain items to automatically inform customers based on their selections. Also, both types of menus allow you to distribute calls to different departments - for example, they can route a call to technical support or to the sales department.
Call history and recording is an important functionality for business. The system keeps statistics of incoming and outgoing calls, tracking their direction, duration and cost. It can analyze the activities of employees and their effectiveness. This also includes the functionality of notifications about missed calls - the manager receives a report on the number of missed calls from existing or potential clients. At the same time, VATS records all conversations for further investigation and improvement of the quality of service.
Recording calls helps train new employees and helps resolve conflict situations with clients.
The following important functions:
- Integration with CRM and other business applications (not all - there is no API) - allows you to track new and repeat customer calls, recording the nature of the calls. This functionality is in demand in large companies with thousands of clients, when they need to track who, when and why contacted the hotline. The system also allows you to make callbacks;
- Audio conferences – functionality for holding work meetings. It is convenient because there is no need to tear employees away from their jobs, especially when they work in other departments and even branches;
- Black and white lists - the virtual PBX from MTS rejects unwanted calls or, conversely, allows calls only from certain numbers. This is the standard functionality of any VATS, available to MTS corporate clients;
- Multi-channel telephone numbers - they accept hundreds of calls simultaneously, without the need for short busy signals. These can be direct landline numbers from any region of Russia or numbers in the 8-800 format. The latter were created specifically for organizing customer support hotlines;
- Full functionality for working with calls - hold, forward, transfer. The PBX will redirect the call according to the specified conditions or according to user actions. If necessary, one user can hold several calls on his number at once. The function of restricting outgoing calls is also supported - for example, you can prohibit a particular group of internal subscribers from calling long-distance or abroad;
- Connecting landline, mobile and IP phones into a single corporate network is the essence - unite all your company’s phones within one PBX and call them using short internal numbers;
- Dividing subscribers into groups - this functionality is in demand in large companies with many departments, divisions, divisions and branches;
- Setting up a call center is a powerful functionality for organizing a customer support line. VATS manages the distribution of calls to consultants, informs clients about their place in the queue or estimated waiting time, and can handle several queues at once if the company operates several support lines at once.
The functionality is really rich, as you can see for yourself by taking advantage of the 28-day test period.
How to connect a cloud PBX
To take advantage of all SIP services provided by MTS, you need to order a call from an expert on this page. The application form contains the following information:
- The name of the company requiring telephony services.
- E-mail address.
- Contact phone number.
- The name and surname of the person who will negotiate on behalf of the company.
You also need to indicate whether the company is an existing MTS customer. Additionally, comments are indicated and files are attached. Next, all you have to do is wait for the expert to call - he will explain the tariffs and service packages, offer the best connection options, and introduce you to the list of necessary documents.
Network access equipment
Workplaces can be equipped with IP phones or VoIP adapters to which regular telephone sets are connected. This equipment allows you to work with calls without using a computer. For workplaces already equipped with computers, the use of softphones is recommended (especially if it is a call center). A microphone with headphones or a headset is connected to each PC.
Also, the virtual PBX from MTS supports the connection of traditional analog lines. This will allow us to cover the maximum number of workplaces, including those without Internet access. Connection of mobile numbers is also supported.
Mobile employees working in the field can use either mobile phones or softphones installed on smartphones.
Feedback from our reader
My company required IP telephony that would meet a number of requirements: the presence of a PBX, the ability to use numbers from different regions, reasonable prices and the ability to quickly resolve issues. I chose from several providers on the market, and finally settled on Zadarma, it meets all our requirements. Read more >>>
Russia: available cities and operators for connecting virtual phone numbers
| City/operator | Region code | Forward to SIP (USD) | Calls | SMS | Fax | Doc. | ||
| Moscow | 499 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Saint Petersburg | 812 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Moscow | 495 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Ekatirenburg | 343 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Izhevsk | 3412 | 10 | 32 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kazan (connection in 5 days) | 8432 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kaliningrad | 4012 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Krasnoyarsk | 3912 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 8312 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Novosibirsk | 3832 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Rostov on Don | 8632 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Tyumen | 3452 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Tula | 4872 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Ufa | 3472 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Arkhangelsk | 8182 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Astrakhan | 8512 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Barnaul (connection in 5 days) | 3852 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Belgorod | 4722 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Byysk (connection in 5 days) | 3854 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Bryansk | 4832 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Zarinsk | 38595 | 10 | 16 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Ivanovo (connection in 5 days) | 4932 | 30 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kaluga | 4842 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kurgan (connection in 5 days) | 3522 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kursk | 4712 | 27 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Lipetsk | 4742 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Magnitogorsk (connection in 5 days) | 3511 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Nizhny Tagil (connection in 5 days) | 3435 | 44 | 44 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Omsk | 3812 | 29 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Eagle | 4862 | 29 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Permian | 3422 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Pskov (connection in 5 days) | 8112 | 50 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Rubtsovsk | 38557 | 10 | 50 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Ryazan | 4912 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Smolensk (connection in 5 days) | 4812 | 35 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Stavropol | 8652 | 29 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Surgut | 3462 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Ulyanovsk | 8422 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Khabarovsk | 4212 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Cheboksary | 8352 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Chelyabinsk | 3512 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Cherepovets (connection in 5 days) | 8202 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Yaroslavl | 4852 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Volgograd | 8442 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| *Mobile Beeline (connection in 2 days) | b-9x | 10 | 23 | + | + | – | — | |
| *Mobile MTS (connection in 2 days) | m-9x | 10 | 23 | + | + | – | — | |
| *Mobile Megafon (connection in 2 days) | mg-9 | 10 | 23 | + | + | – | — | |
| Samara | 8462 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Vladivostok | 4232 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Krasnodar (connection in 5 days) | 8612 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Komsomolsk-on-Amur (connection in 5 days) | 4217 | 49 | 60 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Moscow | 498 | 10 | 15 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Irkutsk (connection in 5 days) | 3952 | 27 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kirov (connection in 5 days) | 8332 | 18 | 32 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Angarsk (connection in 10 days) | 3955 | 54 | 40 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Armavir (connection in 5 days) | 86137 | 39 | 40 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Birobidzhan (connection in 5 days) | 4272 | 44 | 40 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Bratsk (connection in 5 days) | 39533 | 20 | 25 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Chita (connection in 5 days) | 3022 | 44 | 42 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Elabuga | 85557 | 46 | 24 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Engels (connection in 5 days) | 8453 | 26 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kemerovo | 38424 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Khanty-Mansiysk (connection in 10 days) | 346 | 40 | 40 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kolomna | 4966 | 43 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Kostroma (connection in 5 days) | 494 | 43 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Murmansk | 8152 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Naberezhnye Chelny (connection in 5 days) | 855 | 20 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Neftekamsk (connection in 5 days) | 34783 | 37 | 40 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Nizhnekamsk (connection in 5 days) | 8555 | 25 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Nizhnevartovsk (connection in 5 days) | 3466 | 20 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Novoaltaysk | 3853 | 10 | 16 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Novocheboksarsk | 83525 | 27 | 33 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Novocherkassk (connection in 5 days) | 8635 | 60 | 29 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Novokuznetsk (connection in 5 days) | 3843 | 34 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Novomoskovsk | 48762 | 60 | 29 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Novorossiysk (connection in 5 days) | 8617 | 49 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Novy Urengoy (connection in 5 days) | 3494 | 49 | 40 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Noyabrsk (connection in 5 days) | 3496 | 33 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Orenburg | 35323 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Orsk (connection in 5 days) | 3537 | 29 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Peza (connection in 5 days) | 841 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Salekhard (connection in 10 days) | 34922 | 40 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Saransk (connection in 5 days) | 834 | 61 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Saratov | 8452 | 29 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Syktyvkar (connection in 10 days) | 821 | 44 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Taganrog (connection in 10 days) | 863 | 44 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Tambov (connection in 5 days) | 4752 | 44 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Tolyatti | 848 | 20 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Tomsk | 3822 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Tver | 4822 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Ulan-Ude (connection in 5 days) | 301 | 44 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Ussuriysk | 4234 | 60 | 29 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Vanino | 42137 | 60 | 29 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Vladimir | 492 | 10 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Vologda (connection in 5 days) | 8172 | 34 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Volzhsky (connection in 5 days) | 8443 | 29 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Voronezh | 4732 | 27 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Yakutsk | 4112 | 20 | 25 | – | – | – | Any | |
| Yoshkar-Ola (connection in 5 days) | 8362 | 20 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk (connection in 5 days) | 4242 | 40 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| *Mobile Tele2 (connection in 2 days) | t2-9 | 10 | 23 | + | + | – | — | |
| Sochi | 862 | 15 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Crimea, Sevastopol (connection in 5 days) | 8692 | 20 | 50 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Crimea, Simferopol (connection in 5 days) | 3652 | 43 | 40 | + | – | – | Any | |
| *Mobile virtual Moscow (connection in 2 days) | vm-9 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Moscow (Platinum) | 499P | 40 | 85 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Moscow (Golden) | 499G | 25 | 65 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Crimea, Yalta (connection in 5 days) | 3654 | 49 | 60 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Abakan (connection in 5 days) | 3902 | 39 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Dzerzhinsk (connection in 5 days) | 8313 | 20 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Grozny (connection in 5 days) | 8712 | 30 | 30 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Velikiy Novgorod | 816 | 10 | 20 | + | – | – | Any | |
| Volgodonsk (connection in 5 days) | 8639 | 24 | 25 | + | – | – | Any | |
| 800 numbers (Toll Free) | 800 | 15 | 52 | 0.3 | + | – | – | Any |
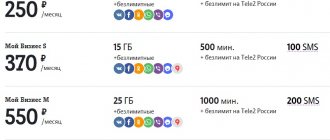
MTS tariffs
| Rate | Multichannel number | Base | Standard | Advanced |
| Price | From 100 rub/month | From 1000 rub/month | From 3150 rub/month | From 7900 rub/month |
| Number of multi-channel numbers (included) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Number of simultaneous calls made | From 1 | From 3 | From 10 | From 30 |
| Number of workplaces | 1 | From 10 | From 30 | From 100 |
| Minutes in your home region and to MTS Russia numbers | – | – | 500 | 2000 |
| Call center – workplaces, pcs. | – | – | From 5 | From 10 |
| Call center – simultaneous calls, pcs. | – | – | From 25 | From 50 |
| Call center – support levels, pcs. | – | – | 1 | 2 |
| Call center - call interception | – | – | – | Yes |
| Call center – music for calls and holds | – | – | – | – |
The cost of calls depends on the selected tariff plan; tariffs are selected in consultation with an MTS expert - they are not published on the official website. Connected mobile phones are serviced at their own rates. Calls within the MTS network are at discounted prices, calls within the company are free.
Additional workstations, free channels for telephone lines and additional functions are paid according to a separate price list.
Comparison with PBX from other providers
Constant competition in the cellular communications market forces other operators to release similar solutions in order to attract more consumers. Let's conduct a small analysis of the features and prices of cloud PBX of popular Russian operators. We will write down all the characteristics in the table for clarity:
| Company name and type of equipment | MTS Basic set | Megafon – Basic | Beeline - Basic | Tele2 Standard set |
| Amount of standing payment, rub. | 1000 | 1000 | 800 | 50 |
| Number of phones in multi-channel mode | 1 | 1 | 1 | Possibility to activate an additional package +1 for 300 rubles |
| Number of employees included in the package | 10 | 7 | 7 | No limits |
| Increase in standard staff | Impossible | + 200 rubles for each new user | + 90 rub. per individual contact | No |
| Ability to record voice communication | Yes | Yes, for an additional fee - 1000 rubles. | Allows for 400 rubles | No |
| Long distance communication | Eat | Eat | Eat | No |
Attention! The article discusses prices and features of providing kits only for corporate clients from the Moscow region. In other parts of the country, characteristics may vary significantly. Check with your local provider representatives for details.
Cloud PBX MTS is a great opportunity to organize high-quality and profitable communication in your enterprise. It helps improve business efficiency and profitability. Choose the right package according to your needs and enjoy multi-channel communication.
Pros and cons of MTS virtual PBX
| Advantages | Flaws |
| PBX from MTS is flexible and allows you to assign individual settings to each user. The control interface is Russified and does not cause any difficulties. You can get acquainted with it during the test period - order test access on the operator’s website. | Many features already implemented by competitors are still in development. Typical examples are call forwarding to voicemail or scheduled forwarding. |
| Ability to work with fax messages - receive and send faxes with per-minute billing. The number of received and sent faxes is not limited. | Low quality of technical support – this is stated by real users on specialized forums. |
| The ability to connect existing office PBXs via trunk allows you to expand existing functionality without replacing equipment or refurbishment of workstations. | There is no clear information on telephony tariff plans - you need to find out everything from MTS specialists. |
| Expanded functionality for call centers - all features are separated into a separate group. Here you can set up flexible call distribution conditions, divide employees into groups, form queues of subscribers, provide them with help and technical information automatically, using pre-recorded single-level and multi-level menu items. |
How to buy a mobile virtual phone number:
- Register on the site or log into your personal account if you have already registered;
- Top up your balance with the cost of connecting the number and the subscription amount. fees for 1 month (and do not forget to leave funds for forwarding or outgoing calls);
- Choose a country;
- Select room type;
- Select a city (*Mobile +…);
- Set forwarding settings;
- Select the period for which you want to buy a number: 1, 3, 6 or 12 months (2-18% discount depending on the subscription period and room price);
- Check your details and complete your order.
When the number is connected (within 24 hours or longer, depending on the type of number and the need to verify your documents), you will receive an email with information about your number.
We provide the opportunity to buy an MTS phone number in a current country, for example, Russia with the code +7-91 or Ukraine (the new name of the Vodafone brand, code +380-99) and many other countries.