IP address (internet protocol address) in a broad sense is the address of a specific network node based on the IP protocol. To put it simply, each computer or device that connects to the Internet receives a unique IP address, and it looks like a set of four numbers from 0 to 255 - dots are placed between them. This is the so-called “external” IP address, that is, the one with which you access the Internet. You can find out the IP on specialized sites - for example, here).
In addition to the external IP address, there is also such a thing as local IP, that is, an address within the network of a particular provider. The fact is that there is a shortage of external IP addresses in the world, and providers often give the same IP address to several clients. But at the same time, within the network of the provider itself, each computer receives a special local IP, which is not used to access the global web.
An external IP address can be static, that is, constant, and dynamic, which changes every time you reconnect to the Network, reboot the router, and so on. Many users, noticing that their IP address has changed, begin to wonder whether everything is okay, whether their computer has been hacked, and so on. Now we will try to figure out what the advantages and disadvantages of dynamic and static IPs are and how to get the type of address you need.
The difference between “statics” and “dynamics”
Before you learn how a static IP differs from a dynamic one, you need to understand the principle of its formation. In 1981, the fourth version of the Internet Protocol - IPv4 - was introduced. It began to be used everywhere, for all computers.
The protocol uses a 32-bit binary number divided into 4 bytes or octets to specify an address. Therefore, there can be a total of 2 to the thirty-second power, which is approximately equal to: 4,294,967,296 numbers or IP addresses. Writing identifiers in binary was inconvenient, and they were converted to decimal places.
Each computer on the network was assigned a fixed unique number, and it did not change over time. At first it seemed that more than 4 billion static IP addresses would be enough for all network participants. But by the end of the 80s of the 20th century it became clear that the limit would soon be exhausted.
Now we can explain what dynamic IP addresses are. Most users are not online 24/7 and their static reserved IDs are not used. It was proposed that during the client’s absence, his unique number should be assigned to an active member of the network, and a new one assigned to him at the next contact.
The network user no longer received permanent IP addresses, but dynamic ones - changing with each connection. This made it possible to optimize the distribution of identifiers. It turns out that one “IP address” can connect several users at different times. The DHCP protocol was developed, which automatically assigned addresses to clients for a certain time.
Brief afterword
In conclusion, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that novice users often confuse the terms “gray” and “dynamic” or “static” and “white” address, unfairly believing that they are the same thing. Please note that both gray and white IP can be either static or dynamic.
Now it would be useful to note what advantages each type of individual entrepreneur has. The question is ambiguous, since it all depends on who may need one or another type and for what purposes. Therefore, it is more logical to talk not about their advantages, but rather about their features. Let's say a static external IP address allows :
- create your own server, including a game server
- seamlessly and efficiently work with torrents (a special protocol through which users download files from each other’s computers)
- increase the security of your account on any service or the security of your own web resource if linked by IP
- connect remotely to your home computer, if, of course, the appropriate settings are made
But here are the opportunities provided, for example, by having a dynamic address :
- if you receive an IP ban on some resource, after a while you will be able to access it again
- use of file hosting services in a free version (many such services limit free downloading)
- your PC or other electronic device is more difficult to use as a target for attack by various types of hackers
In general, as elsewhere in our lives, there is no ideal. Each option has its pros and cons, so you should choose based on the purpose for which your device will be used to access the Internet.
"White" and "gray" identifiers
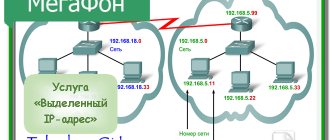
Static and dynamic IP addresses have one more characteristic. They can be internal or external. Also, internal identifiers can be called “local”, “gray”, “private”, and external identifiers can be called “global”, “white”, “public”.
“White” numbers – have direct access to the Internet without a router or router. They can both send and receive data from any computer on the network. A small fee is charged for an external IP address. Having a public number is required in the following cases:
- The computer is used as a server in online games or a host.
- You need remote access to a PC or video surveillance system.
- Download information from servers without queueing.
- Cannot "bypass" router or router.
“Gray” identifiers cannot be used on the Internet. They are used in local networks that do not have direct access to the global network. They are distributed free of charge by your ISP or router. The following ranges are allocated for them:
- From 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255;
- From 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255;
- From 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255;
- From 100.64.0.0 to 100.127.255.255.
All routers organize a local network that unites computers with internal identifiers. The router has one or more external addresses through which it connects to the Internet. These are called WAN ports. Local devices connect to the global network via NAT technology. It sends requests from “grey” numbers and receives responses from outside.
The advantages of internal IDs include security and free use. It is impossible to carry out a virus attack on a local number from outside; it is under the “protection” of the router. But it cannot be used for a server, since it is not capable of responding to requests from the Internet.
Why is external IP dangerous?
The main danger of an external IP address is the same as its advantage: it allows you to connect to your device directly from the Internet. From anywhere in the world, to anyone - that is, to attackers too. Then, using certain vulnerabilities, cybercriminals may well get to your files and steal some confidential information, which they can then either sell or blackmail you with it.
In addition, an attacker can change your Internet access settings, for example, force the router to give you phishing copies of some sites instead of them - then all your logins and passwords will be stolen very quickly.
How do hackers know who to attack? Firstly, there are public Internet services that regularly check all IP addresses in a row for vulnerabilities and allow literally in a couple of clicks to find thousands of devices that have one or another hole through which they can be hacked. Secondly, if they wish, attackers can find out exactly your IP - for example, through running Skype. Your address is also visible when you simply visit website pages.
By the way, using a real IP address you can not only hack your home network, but also launch a DDoS attack on you, sending you many packets from different devices at the same time and overloading the Internet channel and router. Your Internet provider has protection against this, what about you? Such attacks are often carried out against gamers and streamers - for example, to “throw out” a strong opponent from a competition by “clogging” his Internet.
How to protect yourself
The best way to protect yourself is, of course, not to use an external IP address at all, especially if you are not sure you need one. Don't be fooled by ISP advertising, no matter how convincing it may be.
If you are sure that you need a direct IP, then first of all change the default password for the router. This will not protect you from hackers exploiting vulnerabilities of a specific device model, but it will save you from less skilled attackers. It would be a good idea to use a router model that has fewer holes known and popular among hackers - although, to understand this, you will have to scour the Internet thoroughly.
It is advisable to update the router firmware regularly - newer firmware versions usually fix errors that were found in earlier versions. And, of course, you need to enable all available built-in security measures in the router - in home models these are not the most effective solutions, but at least something.
In addition, it is advisable to use a VPN - for example, Kaspersky Secure Connection. Then at least your external IP address will not be visible everywhere you go on the Internet: instead, the VPN server address will be displayed.
Finally, don't neglect security solutions on both computers and mobile devices. Today, they not only catch malware, but also allow you to protect against other types of attacks, such as redirections to malicious sites or the addition of malicious advertising - and these are the types of attacks that are most likely to occur when a router is hacked.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Static Identifiers
The choice between a static or dynamic IP address depends on the purpose of the computer. The advantages of “statics” include:
- More stable connection. A seamless connection is important when authenticating and downloading files. Static IP does not interrupt communication with the server in case of fleeting interruptions.
- If the PC is planned to be used as a host or server, then it needs a static address. If the server has a dynamic IP, then clients will have to verify it each time before connecting.
- Convenient for remote access or using special programs - for example, “TeamViewer”. If you are knocked out of the Internet, then with a dynamic address it will be more difficult to restore access to the desktop.
Along with the advantages, there are also disadvantages:
- Static addresses are more susceptible to hacking. Security measures should be increased when using this identifier.
- Payment is used for the server, then constant presence on the network is paid. The cost may be high.
- Setting up a static “IP address” is more complicated than setting up a “dynamic” one.
Whether a static or dynamic ID is used depends on the tasks being scheduled.
Why is this connection method needed?
Most often, a permanent identifier is needed to use a computer as a server. As a rule, legal entities need such a service to support the operation of web servers or database servers, to create their own VPNs, etc. A permanent connection is more stable, therefore there is less ping and higher Internet speed.
In addition, unchanging coordinates are needed to configure PC control via the Internet (for example, “remote desktop”). However, only a few receive permanent coordinates, upon special request and, as a rule, for a fee. This situation arose for several reasons:
- There are not enough addresses for everyone, and the use of dynamic identifiers allows more devices to access the Internet.
- Permanent coordinates are less secure and are easier to hack or attack.
Dynamic or static IP address: how to find out - the question is easy, you just need to check your ID, reconnect to the network and check the ID again. You can use the following services to check:
- 2ip.ru;
- Yandex.Internetometer.
Changing the digital combination indicates a dynamic connection. If the numbers remain the same (and the user did not order), then most likely the address is still dynamic, and after several Internet restarts it will change.
How to determine an IP address
If the connection occurs through a router, then most likely the computer has an internal dynamic identifier. You can find it out like this:
- Go to the OS Windows control panel.
- In the “Network and Internet” section, click on the “View network status and tasks” item.
- In the window that appears, click on the line “Change adapter settings” on the left.
- A menu with network adapters will open. Double-click on the desired one.
- A window will pop up describing the connection. Click on the “Details...” item.
- The last menu will show the IP address of the PC.
To find out the external identifier, you can use a browser. To do this, you need to enter one of the following sites into it: “2IP”, “WhatIsMyIP”, “IP-Ping”, “whoer.net”. After downloading, the identifier with which you connect to the Internet will be shown.
Well, the most important question: how to make a static IP address from a dynamic one? – You can get a permanent external address in two ways: buy from a provider or use special programs, for example, “No-IP”. You can also use the DDNS functionality - read about this in more detail here.
How to set up a static IP in Windows 7, 8.1 and 10
In the Windows operating system, you can set a static IP address in four ways:
- via the command line,
- through network connections,
- using Windows PowerShell,
- in network settings.
We will show you the two most universal installation methods - through the command line and through network connections.
Method 1. Through the command line
- 1. Press the key combination Win + R.
- 2.
Type “cmd” into the search bar and click OK: - 3.
Enter the command:netsh interface ipv4 show config
Check your network connection name and router gateway:
- 4.
Then run a command like:netsh interface ipv4 set address name="Wireless network" static 123.123.123.123 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1
Where:
- Wireless Network - the name of your network connection,
- 123.123.123.123 - new IP,
- 255.255.255.0 — subnet mask (default value),
- 192.168.3.1 - Gateway.
- 5.
Specify Google's root DNS servers with the commands:netsh interface ipv4 set dns name=”Wireless network” static 8.8.8.8
And
netsh interface ipv4 add dns name=”Wireless network” 8.8.4.4 index=2
Ready.
Why does the IP change?
Some providers quite officially provide dynamic IP addresses. The fact is that the number of unique IP addresses available to the provider may be less than the number of its clients. But since often not all users connect to the Internet at the same time, sometimes providers act as follows: when connecting, the user is given one of the free IP addresses for that minute, and after the end of the access session, this IP returns to the list available to subscribers. However, in our time this is no longer so relevant, because... most people use routers and they are on 24 hours a day.