Every day our lives are rapidly accelerating, the flow of information is becoming denser, and modern people quite rightly want to always be “in the know.” If we talk about smartphones on Android, then now few people are content with the unit as a means only for making calls. Social networks, video communication, Internet surfing and much more require a constant connection to the Internet. Fortunately, ensuring constant access to the network is no longer as difficult as it was just five years ago. Technologies are developing at incredible speed and today the most popular connection standards are 3G and LTE. This is where debates between users begin - like a rope, opinions about these Internet technologies are constantly pulled in one direction or the other. Be that as it may, both standards have both advantages and disadvantages, and it is not entirely advisable to say which is better in the current state of affairs.
What is LTE
Many smartphones support LTE, but not all users yet know what this means.
LTE (literally from English Long-Term Evolution - long-term development, often referred to as 4G LTE) is a communication standard for fast wireless transmission of information in any volume. Designed for smartphones and other mobile devices that require a high-speed Internet connection.
The standard is an intermediate step in the transition from 3G to 4G .
Connecting to such a network significantly increases the data transfer speed of both downloading and uploading. But despite this, it does not reach the technical characteristics adopted for the next fourth generation of communications.
4G and LTE in questions and answers
Let's figure out how to connect LTE and what's good about 4g: questions for Wifire specialists.
– How to connect 4g on my smartphone? Answer: In the same way as connecting mobile Internet of any format. 3g, 4g and lte can be connected at the Wifire provider’s office or directly on the website. Choose the appropriate tariff plan, check out the prices and submit an online request!
– I have already activated the mobile Internet service. How to enable 4g on your phone? Answer: To enable 4G Internet, you need to activate the mobile Internet function on your device. You may need to change the network mode after connecting to the Internet. To do this, you need to select 4G (LTE) in the mobile network settings. Unfortunately, we cannot provide detailed instructions on how to enable 4g on your phone, since the settings menu for different models is significantly different. We can contact your device manufacturer's service center or your communications service provider for assistance.
– What are the advantages of 4G? Answer: The main advantages of 4G include such parameters as data transfer speed, file upload speed to the network (upload) and file download speed (download). High speeds allow us to offer our subscribers uninterrupted wireless communication throughout Russia, and you get fast mobile Internet at an attractive price.
Tariffs can be changed by the operator. Full up-to-date information on tariffs and or by phone indicated on the website.
Data transmission technology
The new generation network provides connection speeds of up to 100 Mbit/s (theoretically maximum speed). In reality, it is an order of magnitude lower , but the technology is still significantly ahead of the previous standard. It is based on MIMO packet data transmission and OFDM coding system. Thanks to the distribution of transmitting antennas, correlation dependence is completely eliminated. In different countries, communication operates on different bands. Even different telecom operators within a country often use different frequency bands.
Mobile communication standard 2G
2 G (or 2 - G ) is an abbreviation for second generation cellular network. 2G cellular networks the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja (now part of Elisa Oyj) in 1991.
Created in 1982 in Europe, a working group called GSM (Group for Mobile Communications) began to study and subsequently develop a terrestrial communication system for integrated use.
By the end of the 80s, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute took the baton in development and study. It was then that the abbreviation GSM received a slightly different definition and became known as the global system for mobile communications.
The commercialization of mobile networks began only in the early 90s of the last century. The main distinguishing feature of 2G from 1G is the digital method of data transmission, rather than analog. Thanks to the emergence of new technologies, it was possible to launch a service that allows exchanging text messages (SMS) and introduce the WAP protocol, thanks to which subscribers have the opportunity to access the Internet from their mobile devices. Despite the fact that the mobile data transmission speed was extremely low and did not exceed 19.5 kbit/second, the introduction of the wireless protocol was a real breakthrough.
Seeing the unprecedented interest of subscribers in the mobile Internet, companies began to actively develop and subsequently implement new generation networks. This is how the 2.5G and 2.7G network appeared - these were a kind of intermediate options that brought users closer to the coveted third-generation network.
2.5G worked on the basis of GPRS technology and assumed packet-based public mobile communications. In the GPRS network, the data transfer speed was increased to 80 kbit/second, although the developers promised 172 kbit/second.
Then 2.7G appeared, working on the basis of EDGE technology, where speed indicators have already reached 150 kbit/second.
Comparison with 3G
If we compare the last two generations of the network, the current one and the one just developing, we get the following conclusions:
- 4G provides data transmission at speeds hundreds of times higher than the previous generation;
- different data transmission technologies, completely packet in the new one and circuit and packet switching in the previous one;
- availability of VoIP in 4G;
- possibility of integration with E-Ultra;
- stability of communication even at high speeds of object movement.
All these are undoubted advantages of the new network. But there are also disadvantages; 3G during its existence can boast of an extensive coverage area. LTE today is present only in a number of large cities in the country.
Third generation cellular standard - 3G
3 G (3-Generation) is the abbreviated name for the third generation of wireless telephony, which is a development of previous 2G technologies and is characterized by advanced wireless technologies, such as high-speed data transfer, access to multimedia roaming.
Despite the fact that all work on the creation of new 3G technology began in the early nineties, the world learned about the third generation network only at the beginning of the two thousandth. The new technology was based on the CDMA standard, which allowed code division multiple access. The 3G generation included five standards at once: UMTS/WCDMA, CDMA2000/IMT-MC, TD-CDMA/TD-SCDMA, DECT and UWC-136, among which UMTS/WCDMA (this standard became the most popular in the Russian Federation) and CDMA2000/ IMT-MC.
- Let's take a closer look at each technology:
- UMTS is a universal technology that was developed specifically for the implementation of third generation networks in European countries. The frequency range within the range of 2110-2200 MHz is used for operation with a data transfer rate not exceeding 2 Mbit/second for a subscriber who is in the same place and no more than 144 Kbit/second for a subscriber on the move.
- HSDPA High-speed Internet with packet data transfer from BS to mobile phone. The first representative of the high-speed Internet family, which is based on UMTS technology. Thanks to this protocol and its subsequent versions, it was possible to significantly increase the speed of mobile data transmission in the 3G network. Initially, the maximum speed under the HSDPA protocol did not exceed 1.2 Mbit/second, in a newer version it reached 3.6 Mbit/second (the most popular version, which is still found in many modems). As the HSDPA protocol improved, it was possible to achieve a data transfer rate of 7.2 Mbit/second and reach a peak of 14.4 Mbit/second. The new version of the technology was DC-HSDPA, where speed indicators reached 28.8 Mbit/second.
- HSPA+ This technology is based on HSDPA, the main difference between the two protocols is the more complex signal conversion and transmission techniques of HSPA+. The maximum speed that can be achieved when working with the HSPA+ protocol is 21 Mbit/second. Some experts call this technology 3.5G.
- DC-HSPA+ Improved HSDPA technology, which managed to “overclock” 3G to a speed of 42.2 Mbit/second. The channel width is 10 MHz, many consider this option to be a dual-channel version of HSPA+, which corresponds to 3.75G.
Each device that supports the 3G network can operate seamlessly in the standards of the other two generations. The same Huawei E173 modem is designed to work with the second and third generations of standards. The maximum at which this modem model can operate is 7.2 Mbit/second. Another model Huawei E3131 (with a maximum data transfer speed of 21 Mbit/second) operates in 2G/3G, but can also support HSPA+, which is not possible in the previous modem model.
However, it should be taken into account that theoretical and real speeds differ, and not in favor of subscribers. If in theory the speed is 3.6 Mbit/second, then in practice it will be 1-2 Mbit/second, or if 7.2 Mbit/second is stated, then in reality the speed will not exceed 3.5 Mbit/second.
In this case, the actual speed will largely depend on the signal level, load indicators of the cellular operator’s base station and other factors. If you are considering the option of purchasing a 3G modem, then it is best to pay attention to the Huawei E3372 model, which can operate in a third generation network supporting data transfer speeds of up to 42.2 Mbit/second, but also 4G networks (theoretical speed reaches 150 Mbit/second ).
Pros of using it on phones and tablets
What benefits does the introduction of new communication standards bring to users?
LTE on the phone:
- watch videos in high quality without delays;
- use of video communications for calls and video conferencing;
- effective use as a router for WiFi distribution.
Increasing data transfer speeds helps expand services and reduce their costs.
Switching 3G to 4G
This transition does not require changing network settings. Activating 4G will allow you to connect to high-speed Internet.
To switch to a high-speed network, the user must perform the following operations:
- Open the main settings menu of your phone or tablet.
- Go to the Mobile networks section.
- Open the More item and go to the Other networks subsection.
- Select Mobile networks.
- Open the Mode item.
The user needs to specify the appropriate connection type. You need to understand that if the communication standard you are interested in is not on the list, the device is not equipped with the required function.
Which operators provide in Russia
All leading companies provide subscribers with this opportunity. Operators also provide users with modems and pocket routers to access the network.
- Megafon has a wide coverage area, but a higher cost of services, unlike its competitors. Offers up to 40 GB monthly; a separate option is connected to access the Internet via LTE.
- MTS has a smaller coverage area. The subscription fee for communication services is lower than that of the previous competitor, and volumes are limited to 25 GB.
- Beeline provides a special SIM card with LTE support. It is worth noting that the coverage area of this operator is wider than that of MTS.
- Tele2 is also introducing LTE. But so far access is only in large cities.
Features of 3G networks
3G or third generation is the technology of the third generation of mobile networks, combining mobile communications and high-speed Internet access. This technology was developed in 1999 and is still relevant today.
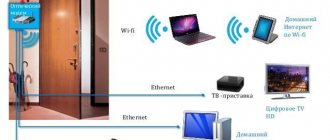
You can connect mobile devices, laptops and desktop computers to 3G networks
3G technology is already built into all modern mobile devices (tablets, smartphones). Moreover, special 3G USB modems are produced, with which you can connect to the mobile Internet via a laptop or desktop PC. If we talk about the advantages of 3G technology, we can highlight the following key points:
- stable telephone connection (even during peak loads on telephone substations);
- advanced data protection system (multi-level coding allows you to ensure the confidentiality of conversations);
- mobility and large network coverage area;
- reduced level of electromagnetic radiation waves (from incoming/outgoing signal) by 4–8 times;
- the ability to use multimedia tools: video calls, media services (listening to online radio, watching Internet videos on various video hosting sites), instant messengers (VKontakte, Telegram, WhatsApp, etc.);
- individualization system - assigning each user an individual IP address, which increases the degree of protection when working on the Internet.
The area of reliable 3G network reception on the map is displayed as blue dots
In addition to the listed advantages, 3G technology also has significant disadvantages in the field of Internet connection:
- low data transfer speed (in a static state of the electronic device, the maximum connection speed reaches 2 Mbit/s; when moving, it can drop to 144 Kbit/s);
- periodic connection failures and general speed instability due to imperfect mobile signal (connection breaks);
- relative inconvenience (different tariffs) and high cost of Internet services. Payment is carried out by automatic debiting of funds from the account in accordance with the traffic used (the situation can be corrected by special tariff plans with a fixed subscription fee);
- 3G USB modems are most often sold configured for a specific operator, that is, the USB modem comes with a SIM card from the corresponding provider for connecting to the Internet. This USB modem will not work with SIM cards from other providers.
SIM cards from other operators will not work in 3G modems from MTS
Choosing 3G is ideal for those users who actively communicate both by phone and on the Internet (using online messengers) . For more serious network tasks (for example, watching online movies in HD quality, downloading large files, etc.), a 3G connection is not the best option.
I decided to conduct a small experiment in order to test the quality of the 3G connection and the performance of the proposed Internet from MTS and Beeline, both on “native” equipment and on third-party equipment. To do this, we purchased two sets from the above-mentioned providers (USB modem and SIM card) and a separate USB modem from the manufacturer HUAWEI (model E8231). After measuring the speed and signal quality on corporate USB modems, both SIM cards were installed one by one into the HUAWEI USB modem. And if in the case of the SIM card from MTS no fundamental changes in the speed and quality of the signal were noticed, then with Beeline some difficulties arose. Firstly, the speed of 3G Internet connected via a HUAWEI USB modem dropped by about 200 Kbps. Secondly, periodic connection interruptions began to occur, which is why I had to either wait for automatic reconnection to the network or restart the modem manually. Therefore, if you decide to purchase a USB modem, then be prepared for the possibility that SIM cards will be incompatible with non-native USB modems.
GPRS
Cellular operators began using the GPRS standard in the early 2000s. The maximum speed reaches 115 kilobits per second under ideal cellular signal reception conditions. This type of mobile connection allows you to download a small page, text information and low-quality compressed images. Streaming video cannot be played. Today GPRS is practically not used due to the low connection speed.
VoLTE - calls over LTE
Surely many of you have noticed the VoLTE function in your smartphone - what it is and why it was created. Many people underestimate her, but in vain. This technology, which is no longer new, allows you to transmit not only traffic, but also voice over 4G.
Simply put, if you have unlimited Internet, then with VoLTE you can talk on the phone as much as you like and completely free .
Another benefit of this feature is battery saving. Due to the fact that voice calls are currently made exclusively via 2G or 3G, during a phone call the device automatically switches from the 4G network to the 3G network, which affects the amount of charge.
And an additional bonus is that you can use the Internet at the same time during a call.
eNodeB functions (Evolved NodeB)
eNodeB combines the functions of base stations and 3rd generation network controllers:
— provides traffic and signaling transmission via radio channel,
— manages the distribution of radio resources,
— provides an end-to-end traffic channel to the S-GW,
— supports synchronization of transmissions and controls the level of interference in the cell,
— ensures encryption and integrity of transmission over the radio channel,
— selects the MME and organizes signal exchange with it,
— compresses IP packet headers,
— supports multimedia broadcasting services,
— when using a structure with power amplifiers on an antenna mast, it organizes antenna control using a special Iuant interface.
S 1 interface , as shown in Fig. 2, supports data transmission from the S-GW and signaling through the MME. Note that the eNB may have connections to multiple S-GWs.
X2 interfaces are used to organize handovers between neighboring base stations, including when balancing the load between them . In this case, X2 interfaces can be logical, i.e. their organization does not require a real physical connection between eNBs.
Functions of the S-GW serving gateway:
— routing of transmitted data packets,
— setting quality indicators (Quality of Service, QoS) of the services provided,
— buffering of packets for UEs in Idle Mode,
— provision of accounting data for tariffing and payment for services performed.
S-GW is an anchor structure that provides subscriber mobility. Each operational UE is served by a specific S-GW. In theory, a UE can be associated with multiple packet networks; then it will be served by several S-GW servers.
PCRF functions
Policy and Charging Resource Function (PCRF) is essentially a control server that provides centralized management of network resources, accounting and charging of services provided. As soon as a request for a new active connection appears, this information is sent to the PCRF. It evaluates the network resources at its disposal and sends commands to the PCEF of the P-GW gateway that establish requirements for the quality of services and their tariffs.
Read more about the technical aspects of the functioning of mobile networks, tariffs, quality of service and much more in the book “Mobile communications on the way to 6G.”
P-GW (Packet Data Network Gateway) functions
The gateway for accessing packet networks P - GW organizes an access point to external IP networks. Accordingly, P-GW is the anchor gateway for traffic provisioning. If the subscriber has a static IP address, then P-GW activates it. If the subscriber must receive a dynamic IP address for the duration of the communication session, P-GW requests it from the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server or performs the necessary DHCP functions itself, after which it ensures delivery of the IP address to the subscriber. P-GW includes PCEF (Policy and Charging Enforcement Function), which provides quality service characteristics on an external connection via the Sgi interface and data packet filtering. When servicing a subscriber on a home network, the P-GW and S-GW functions can be performed by either two different or one device. The S5 interface is a GPRS or Proxy Mobile Ipv6 tunnel connection. If P-GW and S-GW are in different networks (for example, when servicing a subscriber in roaming), then the S5 interface is replaced with the S8 interface.