What do HSPA and HSPA+ internet standards mean, and how are they different?
The HSPA standard is a high-speed mobile Internet that is available to users of modern phones. According to the developers, it has a speed of 14.4 Mbps, so it is ideal for visiting websites, video calling or watching streaming video.
In urban environments, connection speeds are often slower due to electromagnetic pollution and obstacles located between the consumer and the cellular operator's repeater. Typically the information transfer rate is 10 Mbit/s.
Second generation - 2G
In 1982, the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Authorities formed a working group called GSM (French Groupe Spécial Mobile - special group for mobile communications). The purpose of creating the group is to study and develop a pan-European terrestrial mobile communication system for general use. In 1989, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute continued the study and development of the second generation of mobile communications. The abbreviation GSM then acquired a different meaning - Global System for Mobile Communications (global system for mobile communications). In 1991, the first commercial second generation mobile networks appeared. The main difference between second-generation networks and the first is the digital method of data transmission. Digital data transmission technologies made it possible to introduce a text messaging service (SMS), and later, using the WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) protocol, it became possible to access the Internet from mobile devices. The data transfer speed in second generation networks was no more than 19.5 kbit/s. The further increase in user demand for mobile Internet provided the impetus for the development of next-generation networks. The intermediate stages between 2G and 3G networks were generations conventionally called 2.5G and 2.7G . 2.5G generation was designated GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) technology, which made it possible to increase the data transfer rate to 172 kbit/s in theory, and up to 80 kbit/s in reality. 2.7G generation is called EDGE (EGPRS) technology (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution), which functions as an add-on over 2G and 2.5G. The data transfer speed in such networks can theoretically reach 474 kbit/s, but in practice it rarely reaches 150 kbit/s.
Third generation - 3G
UMTS
UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) is a cellular communication technology developed for the introduction of 3G in Europe. The frequency range used is 2110-2200 MHz. (often the channel width is 5 MHz). The data transfer speed in UMTS mode is no more than 2 Mbit/s (for a stationary subscriber), and when the subscriber moves, depending on the speed of movement, it can drop to 144 Kbit/s.
HSDPA
HSDPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access - high-speed packet data transfer from a base station to a mobile phone) is the first of the HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) family of cellular communication protocols, based on UMTS technology. This protocol and its subsequent versions have made it possible to significantly increase data transfer speeds in 3G networks. In its first implementation, the HSDPA protocol had a maximum data transfer rate of 1.2 Mbit/s. The data transfer rate in the next implementation of the HSDPA protocol was already 3.6 Mbit/s. At this point, 3G modems became very popular and most users had modems that supported this particular standard, the most popular models being Huawei E1550, ZTE mf180 (such examples are still found today). As a result of further development of the HSDPA protocol, it was possible to increase the speed first to 7.2 Mbit/s (the most popular modems are Huawei E173, ZTE MF112), and then to 14.4 Mbit/s. (Huawei E1820, ZTE MF658) The pinnacle of HSDPA technology was DC-HSDPA technology, the speed of which could reach 28.8 Mbit/s. DC-HSDPA is essentially a two-channel version of HSDPA.
HSPA+
HSPA+ is a technology based on HSDPA, which implements more complex signal modulation methods (16QAM, 64QAM) and MIMO technology (Multiple Input Multiple Output). The maximum 3G speed can reach 21 Mbps. A similar technology is already classified as 3.5G .
DC-HSPA+
DC-HSPA+ technology with the fastest 3G Internet 42.2 Mbit/s. This is essentially two-channel HSPA+ with a channel width of 10 MHz. This technology is often called 3.75G .
All devices that support third generation networks also support the standards of previous generations. For example, the now outdated Huawei E173 USB modem for 2G/3G networks supports GSM, GPRS, EDGE (up to 236.8 Kbps), UMTS (up to 384 Kbps), HSDPA (up to 7.2 Mbit/s), i.e. network standards of both second and third generations. The maximum speed with which this device can operate is 7.2 Mbit/s. The more “advanced” model Huawei E3131 for 2G/3G networks supports a set of standards, including, in addition to the above, HSPA+. The maximum achievable download speed on this device is much higher and is 21 Mbit/s. But it should be taken into account that the maximum theoretical and real speeds differ quite significantly. For example, on Huawei E1550, zte mf180 modems, where the maximum speed is 3.6 Mbit/s, in practice you can achieve a speed of 1-2 Mbit/s, on Huawei E173, ZTE MF112 modems (maximum speed 7.2 Mbit/s) in practice 2-3.5 Mbit/s, this is subject to good signal level and low load on the mobile operator tower. One of the factors for increasing 3G Internet speed is to use a modem that supports maximum 3G speed. We recommend the Huawei E3372 ; it not only supports maximum 3G Internet speed (up to 42.2 Mbit/s), but also 4G (up to 150 Mbit/s). Someone may object and say that there will never be 4G in their “hole,” but don’t forget that a few years ago you didn’t even dream about 3G. Technology does not stand still!
HSPA Specifications
The first generation networks corresponded to the spirit of the times - for those times, 10 Kb/sec was not a bad indicator at all, given that cell phones of that time practically did not connect to the Internet. But the rapid development of technology led to the emergence of second-generation networks, which used several independent protocols. Some of them have survived to this day - for example, GPRS with speeds of up to 171 Kb/s, as well as EDGE with twice the speed (384 Kb/s).
Phones with 2G support could already surf on text versions of sites (WAP technology, many should remember it). The proliferation of smartphones forced developers to look for further ways to increase speed, and the development of the HSPA standard made it possible to move to third-generation networks, which are the most common today.
The maximum download speed using the HSPA protocol was 14.4 Mb/sec. Theoretically, this is enough to watch high-resolution videos on a small screen. The data upload speed is lower - 5.76 Mb/sec, but for ordinary users it is the downlink that is important. True, in reality the numbers again turned out to be far from the maximum, due to the presence of many limiting factors.
Theoretically, the appearance of MIMO technology in 3G networks would have more than doubled the speed, but it was not possible to implement 64QAM and MIMO at the same time, so in the HSPA+ standard the speed was increased relatively slightly, to 21 Mb/sec.
But the breakthrough was not long in coming: in the eighth specification of the standard, developed in 3GPP, called DC-HSDPA, the downlink speed was increased to 42 Mb/sec, and the uplink speed to 11 Mb/sec.
The HSPA protocol in its pure form and with later variations is supported by almost all mobile devices; the presence of 3G support in the device specification is sufficient. Coverage is another matter: at the moment it is not available everywhere, since the deployment of high-speed networks is a financially expensive undertaking for mobile operators.
If you doubt whether you can take advantage of the speeds available on 3G networks in a particular area, ask your provider; they will not refuse to provide you with a coverage map.
Fifth generation - 5G
Work on developing new standards for wireless data transmission continues unabated. Mainly with the sponsorship of one of the largest manufacturers of network equipment, the Chinese company Huawei. The widespread introduction of fifth-generation technologies is predicted in 2021. There is no clear information regarding the maximum data transfer speeds in 5G networks yet, but it is known that in pilot tests of 5G networks it was possible to achieve speeds of 25 Gbit/s. This is tens of times higher than the maximum data transfer rates in fourth generation networks.
•
Our service center installs 3G antennas in Krasnodar and the Krasnodar region. Specialization in the field of installation of antenna equipment requires knowledge of the material base used and the technologies embedded in this material base. One of the technologies used to increase data transfer speeds in wireless networks is called HSPA+ . So let's figure out what this HSPA+ technology is.
Conceptually. Mobile operators were looking for a way to increase the profitability of their mobile services business. And they found it - the provision of wireless data transmission services. For such data transmission, operators chose technology existing on the data transmission equipment market. Once upon a time this technology was GPRS, then it was replaced by EDGE.... Subsequently, technologies replaced each other and finally grew to a data transmission method called 3G. According to its characteristics, 3G turned out to be such that it suited both telecom operators (in terms of implementation and operation price parameters) and subscribers (in terms of equipment purchase price/speed/subscription fee).
In general, it so happened that 3G turned out to be so good that they began to “pump” it and modernize it. And within the framework of 3 Generation equipment, HSPA reception and transmission technology appeared.
HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access) - high-speed packet access - a technology that combines the possibility of high-speed packet access in the downstream channel (HSDPA - High
-
Speed Downlink Packet Access
) and the possibility of high-speed packet access in the uplink (HSUPA -
High
-
Speed Uplink Packet Access
) channel.
Downlink _
) is a channel for receiving data by the subscriber device.
Uplink _
) is a data transmission channel by the subscriber device.
The data transfer rate for HSDPA can reach 14.4 Mbit/s , for HSUPA – 5.76 Mbit/s . HSPA technology also allows you to increase the throughput of UMTS networks and significantly reduce the time delay. To exploit the full potential of the wide WCDMA band (5 MHz), the performance of HSPA radio communications networks (spectral efficiency, maximum data rate and time delay) will be further improved.
HSPA+
(an abbreviation for
Evolved High-Speed Packet Access, i.e., developed high-speed packet access) is a development of HSPA technology.
In some sources, HSPA+ technology is classified as the 3.75G generation, i.e., indicating that its characteristics are close to the capabilities of fourth generation (4G) networks.
The development of HSPA+ in relation to conventional HSPA is that more complex modulations of a higher order have been added - 16QAM (uplink) / 64QAM (downlink), technology has been added using multiple antennas for the downstream channel (multiple input/multiple output or so-called MIMO). The protocol has been modified to provide support for a larger number of connected network users. The application of the described improvements allows, under optimal conditions, to achieve a maximum data transfer rate in the downstream channel of 28 Mbit/s, and in the outgoing channel - 11.5 Mbit/s with a transmission and confirmation time of less than 30 ms (so-called PING).
The innovations listed above apply to HSPA+ Release 7 of 3GPP.
Subsequently, HSPA+ edition 7 of 3GPP was upgraded. The most important innovation was the emergence of the ability to operate with two carriers (dual carrier or otherwise DC HSPA ) in the downstream channel and the joint use of a multiple-antenna scheme (MIMO) and a 64QAM modulation scheme. Both of these features make it possible to achieve a maximum downstream data transfer rate of 42.2 Mbit/s .
Source of illustration - www.sibir-ix.ru
At the same time, voice channel switching using HSPA technology provides optimal support for telephone services in any packet-switched radio network using it. In addition, by forming a common enhanced dedicated channel (E-DCH) for the CELL_FACH state and carrying out layer 2 modifications in the uplink, latency is further reduced.
The listed innovations already apply to HSPA+ Release 8 of 3GPP.
The above capabilities of HSPA+ technology are impressive. The speeds that are achievable with its use can potentially provide users with a very comfortable stay on the Internet. But the development of technology does not stand still, and its next “upgrade” is already planned. The developers' technology development plans (ROAD MAP) are shown in the image below:
As you can see, we intend to further develop high-speed Internet technologies. So, with their proper implementation, you can count on an increase in the speed of Internet access and, most importantly, on its distribution not only in large cities, but also in other territories of our vast country that are not spoiled by high-speed wired Internet.
PS - ATTENTION! This material is not finished yet. Can be corrected and improved. All the facts presented in it should be taken critically, and if you find errors in it, please point them out in the comments and we will correct them.
————————————————————————
Cornices in Krasnodar - non-stainless steel products
————————————————————————
The HSPA standard is a high-speed mobile Internet that is available to users of modern phones. According to the developers, it has a speed of 14.4 Mbps, so it is ideal for visiting websites, video calling or watching streaming video.
In urban environments, connection speeds are often slower due to electromagnetic pollution and obstacles located between the consumer and the cellular operator's repeater. Typically the information transfer rate is 10 Mbit/s.
UMTS and LTE frequencies in Russia: new generation standards
GSM-Repiters.RU » UMTS and LTE frequencies in Russia: new generation standards
the GSM 900, GSM E900, GSM 1800 standards contributed to the improvement of communication channels, but did not solve the problem of access to the Internet at the level required by modern people.
These standards belonged to the second generation (2G), in which the EDGE and GPRS protocols were used for data transmission, which made it possible to achieve speeds of up to 473.6 Kbps - catastrophically low for a modern user.
Today, cellular communication standards determine one of the most important requirements: data transfer speed and signal purity. Obviously, this affects the development of the mobile operator market. So, at one time, 3G networks appeared in Russia, which won the massive attention of users. And now it is for this reason that the number of people who choose 4G is increasing.
Feature of the UMTS standard
The main feature that distinguishes the UMTS standard from GSM is that the use of WCDMA, HSPA+, HSDPA protocols allows users to access higher quality mobile Internet. At speeds from 2 to 21 Mbit/sec, you can not only transfer more data, but even make video calls.
UMTS covers more than 120 largest Russian cities. This is the standard in which the currently popular mobile operators (MTS, Beeline, MegaFon and Skylink) provide 3G Internet service.
It's no secret that high frequencies are more efficient for data exchange. However, Russia has its own nuances that make it impossible to use, for example, UMTS frequency 2100 MHz in some regions.
The reason is simple: the UMTS 2100 , which is actively used for 3G Internet, quickly dries down on obstacles. This means that a high-quality signal is hampered not only by distances to base stations, but also by increased vegetation. In addition, some regions are practically closed to this frequency due to the operation of air defense systems. Thus, in the South-Western part of the Moscow region there are several military bases, and accordingly, an unspoken taboo has been introduced on the use of this frequency.
, UMTS 900 is used for 3G Internet . Waves in this frequency range have higher penetrating power. At the same time, at this frequency the data transfer rate rarely reaches 10 Mbit/sec. However, considering that just a few years ago many cities could not even think about Internet coverage, this is not so bad.
At the moment, Huawei E352 and the more stable version E352b, as well as E372, E353, E3131, B970b, B260a, E367, E392, E3276 are showing excellent results with the popular UMTS900.
LTE: in what ranges will the future standard operate?
The logical development of UMTS was the development in 2008-2010. LTE is a new standard, the purpose of which is to increase signal processing speed and throughput, and in technical terms, to simplify the network architecture and thereby reduce data transfer time. In Russia, the LTE network was officially launched in 2012.
It is LTE technology that determines the development of the new generation of mobile Internet in our country – 4G. This means access to online broadcasts, fast transfer of large files and other advantages of the modern Internet.
At the moment, 4G Internet is supported by the LTE 800, LTE 1800, LTE 2600 standards, using the LTE Cat.4, Cat.5, Cat.6 protocols. This allows, in theory, to obtain data transfer speeds of up to 100 Mbit/s for upload and up to 50 Mbit/s for reception.
High LTE frequencies are becoming an ideal solution for regions where the population density is quite high and where such data transfer speeds are very important. These include, for example, large industrial cities. However, if all operators begin to work only in the LTE 2600 , a problem with radio signal coverage will immediately arise.
Now residents of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Krasnodar, Novosibirsk, Sochi, Ufa and Samara can take advantage of 4G technology. In Russia, Yota became one of the first operators to develop the fourth generation of mobile standards. Now they have been joined by such large operators as Megafon and MTS.
LTE 1800 is considered optimal today : this frequency is more economical and allows new companies that offer mobile communication services to enter the market. It is even cheaper to build networks at 800 MHz. Thus, we can predict that LTE 800 and LTE 1800 will be the most popular among operators and, accordingly, with you.
LTE frequencies of various mobile operators
— Megafon: LTE frequencies 742.5-750 MHz / 783.5-791 MHz, 847-854.5 MHz / 806-813.5 MHz, 2530-2540 MHz / 2650-2660 MHz, 2570-2595 MHz (license for Moscow and Moscow region);
- MTS: LTE frequencies 720-727.5 MHz / 761-768.5 MHz, 839.5-847 MHz / 798.5-806 MHz, 1710-1785 MHz / 1805-1880 MHz, 2540-2550 MHz / 2660- 2670 MHz, 2595-2620 MHz (license for Moscow and the Moscow region);
— Beeline: LTE frequencies 735-742.5 MHz / 776-783.5 MHz, 854.5-862 MHz / 813.5-821 MHz, 2550-2560 MHz / 2670-2680 MHz.
— Rostelecom: LTE frequencies 2560-2570 / 2680-2690 MHz.
- Yota: LTE frequencies 2500-2530 / 2630-2650 MHz.
- Tele2: frequencies 791-798.5 / 832 - 839.5 MHz.
Signal amplification at different frequencies
When you find yourself in an area of uncertain signal reception or move a long distance away from your operator’s base station, you cannot do without an additional antenna.
Directional antennas UMTS 900 signal has a basic configuration and can significantly increase the level of communication. At the same time, not only the Internet connection becomes more stable, but also the quality of voice transmission during a telephone conversation. You can't do without a UMTS 2100 antenna if you want to use the Internet while traveling: due to constant switching from tower to tower, the data transfer speed drops catastrophically.
Directional LTE 800 antennas and LTE 1800 antennas are the best option for amplifying the 4G signal in the corresponding frequencies. These standards have higher signal penetration and range.
However, LTE 2600 has a higher data transfer speed, thanks to which 80% of users in Moscow have already switched to this standard. And purchasing an LTE 2600 antenna is a prerequisite for those who chose 4G LTE 2600 (Megafon, MTS, Beeline, Rostelecom, Yota) in order to get maximum Internet speed. LTE signal amplifier will guarantee stable data transmission at high frequencies.
Solutions from GSM-Repeters.RU
| LTE 800 | |||
| LTE 800 antennas | Modems | Routers | |
| GSM 900 / UMTS 900 | |||
| Antennas | Repeaters | ||
| GSM 1800 / LTE 1800 | |||
| LTE 1800 antennas | Repeaters 1800 | Modems | Routers |
| UMTS 2100 | |||
| 3G antennas | 3G repeaters | 3G modems | 3G routers |
| LTE 2600 | |||
| 4G antennas | 4G repeaters | 4G modems | 4G routers |
GSM-Repitery.RU specialists continue to explore new technologies in the cellular communications and high-speed Internet market. Thanks to this, we quickly provide customers with the necessary equipment to enhance the signal.
At your service in the Catalog are various options for antennas and repeaters that will help you obtain a high-quality signal even in extreme conditions.
HSPA speed and performance
Mobile Internet has always been in great demand. The first GPRS-enabled phones allowed users to browse specially prepared WAP sites. Over time, operators have improved data transmission technologies, creating the EDGE standard. It belonged to the second generation and had a maximum speed of 474 kbit/s.
The third generation of communications served as the beginning of high-speed mobile Internet. It combines the HSPA and HSPA+ standards. After the creation of the new standard, users were able to comfortably visit websites, download large files and watch streaming video. Video calling has also started to develop.
Today, HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) Internet is present in every modern smartphone and is available for fast connection. To do this, you need to check whether the telecom operator supports the 3G standard and look at the network coverage in the desired locality.
Benefits of HSPA:
- High information transfer speed, capable of reaching 14.4 Mbit/s (subject to ideal conditions).
- The ability to visit computer sites, watch videos, download large files.
- Favorable connection prices for most mobile operators, availability of traffic packages or unlimited access.
Flaws:
- Lack of coverage in small towns - even if the smartphone supports HSPA, you will not be able to use the Internet.
- High load on the radio communication module, quickly draining the battery of the mobile device (relatively speaking).
DC-HSPA+
The two-channel HSPA version, as in the case of HDSPA, has doubled the information transfer speed, which is 42.2 Mb/s . This standard is known to many as “ 3.75G ”. In addition, the standard is popular for use in mobile routers, as well as modems (although their use is becoming less and less popular). It is worth noting that almost every DC-HSPA smartphone is presented in the mid-budget segment.
Users also have a question: “HSPA, is it 3g or 4g?” and here the answer is: “3G” will not be 100% correct. What does it mean? DC-HSPA is comparable in speeds and throughput to 4G, although it is considered “3.75G”
Implementation
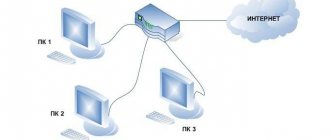
Like all modern communication standards, 3G requires the construction of towers (antennas) that will be responsible for data transmission. Due to the not particularly high cost of introducing the technology, it is used by all mobile operators in the post-Soviet space, although in more developed countries it has been replaced by 4G . Also, thanks to the use of different frequencies and protocols, in crowded places there is no loss of Internet speed characteristics.
HSDPA - what is it? What does it mean in detail?
What is the difference between HSPA and HSPA+?
Today, mobile operators offer the HSPA+ service, which is an improved HSPA standard. It allows you to use the Internet at a speed of 42.2 Mbit/s.
How to use HSPA (High Speed Packet Access):
- Check your phone's technology support. To do this, use the operating instructions, which list the communication standards supported by the device.
- Buy a SIM card from a mobile operator that provides high-speed mobile Internet and subscribe to a favorable tariff.
- Top up your account with the required amount to activate the selected tariff plan and use high-speed Internet.
- Receive configuration settings on your smartphone via SMS (usually sent automatically). You can also use your personal account to independently make the necessary settings in the memory of your mobile device.
- Launch your browser and wait until your phone connects to the Internet. The connection usually takes a few seconds. After successful connection, you will be able to visit any website, download files or watch online videos. It is recommended to control traffic consumption so as not to exceed the operator's limit and not incur unintended monetary expenses.
If the HSPA is not working well, it is recommended to go into an open space. Internet operation may be obstructed by reinforced concrete structures or similar barriers.
What is the difference between HSPA+ and HSPA
The main difference is speed indicators. HSPA has a maximum speed of 14.4 Mb/s, HSPA+ has a maximum speed of 21.6 Mb/s. The difference is not so big that you should worry about it if your phone only supports the first protocol. But such a smartphone is still worth looking for - most cell phones have long switched to the HSPA+ standard, including many models of push-button devices, which by and large are not intended for using high-speed Internet.
But if you are interested in which protocol your phone supports, then when performing actions that require maximum speed (for example, when downloading a large file), try to find the position of the device at which the H+ symbol appears in the status bar.
This will mean that the phone supports HSPA+ and in this situation the download speed will increase significantly. Note that in 3G networks the terrain is important. The presence of artificial and natural obstacles has a strong impact on data transmission speeds, so the best signal will always be in open areas.
Note that the dual-channel implementation of HSPA+ made it possible to increase the theoretical speed limit to 42.2 Mb/sec, but with coverage here things are even worse, and cellular operators are already in full swing deploying 4G networks and testing fifth-generation networks.
Is HSPA still relevant in 2019?
Today, many smartphone owners use HSPA Internet to surf the Internet. The standard is especially popular in small towns where there is no 4G coverage. It is expected that HSPA communications will remain common for several more years until mobile operators offer subscribers faster connections.
Third generation mobile networks are characterized primarily by increased data transfer speeds, which is due not so much to the standard as to the technologies integrated into the standard. In this article we will talk about HSPA technology, which will be useful for active Internet users, as well as for general development.
Development in Russia
The technology has been characterized by rapid development since its inception - today, in Russia, almost all operators offer such a connection to the network.
The most common generation of mobile communications is the third, which has covered the entire world, including our country. The largest networks operate at frequencies of 2000-2100 MHz and have data transfer rates from 2 to 14 Mbit per second. This list includes various add-ons.
The third generation of communications allows you to use the Internet at high speeds and enjoy all the benefits of high-speed traffic. The largest operators (Megafon, Beeline, Tele2, MTS) ensure uninterrupted network operation in almost all large populated areas.
We explained in detail what it is - HSPA on the phone. Now you know the features of using the option, its characteristics and distribution.
What is HSPA
HSPA is an abbreviation for High Speed Packet Access, which translates from English as high-speed data transfer. The protocol is used in 3G networks of the UMTS standard. The emergence of HSPA was facilitated by the low speed of access to the UMTS standard network. Initial expectations for Internet speed were up to 2 Mbit/sec, which by the standards of the early 2000s was quite high. In practice, the speed did not exceed 200-300 Kbps. Therefore, to solve this problem and increase speed indicators, HSPA technology appeared in 2006 as an addition to UMTS networks.
Further development
With the introduction of HSPA, it was possible to lay down the technology with the highest data transfer speed. The next protocol, called HSPA+, made it possible to increase the speed to 21.1 Mbit, and later to 42.2 Mbit. At the same time, it was impossible to obtain the maximum declared speeds, since 42.2 Mbit is the technical speed for transmitting service information. At best, actual speeds reached 30 Mbps under ideal conditions.
The maximum possible data transfer rate in a third generation network with the latest DC-HSDPA w/MIMO protocol is 84.4 Mbit. And in the developing DC-HSDPA w/MIMO, HSPA+ protocol, the data transfer rate is expected to increase to 670 Mbit. Exact data will appear after the approval of the standard documentation.
Background
The development of 3G networks occurred thanks to the development of communication protocols:
- The first protocol was UMTS , which had its own frequencies for operation and a minimum, although high for its time, data transfer speed of up to 2 Mb/s .
Note. The actual speed of the communication standard is usually less than the declared one. This is influenced by network congestion, bandwidth, user speed and the number of obstacles that are located on the signal path to the user. It is worth noting that the UMTS standard was used in usb modem from different companies, while only EDGE was developed in phones
- After which HDSPA appeared - the first of the HSPA protocols . Its distinctive feature was its high speed and throughput. During its improvements, the maximum transfer speed reached 14.4 Mb/s .
- DC-HSDPA is a two-channel edition of the previous standard, which received transfer speeds of up to 28.8 Mb/s .
And only after these stages of formation, the first version of the HSPA network in its pure form appeared - HSPA+ .
It is difficult to name the dates of technology development, but the first implementation at the user level already existed in the late 90s, and the first smartphone that could use the 3rd generation Internet came out in 2002. It was produced by the popular company Nokia.
Megafon 4G - coverage area, tariffs and Internet speed
Where is HSPA used?
HSPA technology is used in all devices that use the third generation cellular communication standard UMTS. We are talking primarily about phones, smartphones and tablets with the function of making phone calls. HSPA is also used in USB modems.
At the same time, most modern smartphones operate on the HSPA+ protocol with a maximum reception/upload speed of 42.2/5.76 Mbit. This is due to the presence of a fourth generation network, where the minimum download/upload speed reaches 150/50 Mbit.
HSPA+
HSPA+ is the same 3G that everyone uses or has used today. It is characterized by download speeds of up to 21.6 Mb/s , upload speeds of up to 5.76 Mb/s . HSPA frequency varies from 2100 MHz to 2200 MHz . The network ping rate is 30 m/s, which allows you to download online content with minimal delays. It implements more complex modulations and also uses MIMO technology, which increases the channel bandwidth. This standard is widely known as “ 3.5G ”.
Conclusion
This article explains in detail what HSPA is. The technology has made it possible to increase data transfer speeds in the third generation cellular network. And the development of new protocols allows for even faster throughput. And although the data transfer speed is inferior to 4th and 5th generation networks, the quality of coverage of the 3rd generation network is higher. Therefore, users living far from large populated areas will be able to use high-speed Internet not only for communication, but also for downloading various data.
What questions do you have? Ask and share your opinion in the comments below the article.
Sources used:
- https://net-well.ru/stati-o-3g-4g-internete/chto-takoe-2g-3g-umts-hsdpa-hspa-dc-hspa-i-4g-lte
- https://tech.servis23.ru/%d1%87%d1%82%d0%be-%d1%82%d0%b0%d0%ba%d0%be%d0%b5-hspa-hspa/
- https://androidlime.ru/hspa-and-hspa-plus-internet-standarts
- https://androfon.ru/article/hspa-chto-eto
SHARE Facebook
- tweet
Previous article
Next articleFull reset of HTC settings (hard reset)