IP telephony is one of the constant expenses for a business, along with payment for office rent, Internet, office supplies and other products of constant consumption. It’s natural that you want to somehow optimize these costs! If you've ever looked for ways to reduce your IP telephony costs, you've probably come across a proposal to use a GSM gateway.
In short, the idea is this: you can select 5 SIM cards from the most common operators, connect the most favorable tariffs, and when you call, the system itself will select the gateway channel (read, SIM card) that is most profitable when calling exactly this number . That is, with a gateway you can build a more flexible system for communication.
It would seem that this is the ideal solution! But no.
SIP-GSM gateways have their own pitfalls. And these pitfalls are quite serious.
What is a GSM gateway and how does it work?
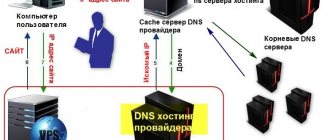
A device called a GSM gateway, obscure to the common man, is used to convert an analog signal into a digital or IP telephony signal, and traffic can be transmitted in any direction; such equipment is also called a bridge.
All these formats differ in a number of characteristics and parameters, so it is impossible to connect them directly. The device is capable of converting and transferring a call from a landline number to a cell phone or digital PBX in the office.
Such gateways serve primarily to save money, but in addition, when connected to a computer, the device can perform the functions of a secretary, for example, voice a greeting, record conversations, and also monitor and account for incoming and outgoing calls in the office, which is very convenient for a manager.
The work flow looks like this. When, for example, a signal from a city line arrives at the device, it converts it and sends it to a cellular phone, PBX or IP network. In this case, the land line equipment perceives the call as a normal one, from a landline to a landline phone. The system works in the opposite direction in the same way. As a result, device owners pay only for calls within a city or cellular network.
Varieties
First, let's briefly understand the terms.
- Analog communications are city PBXs.
- Cellular or mobile communications are already a digital signal that is transmitted within a cellular network.
- To summarize, IP telephony refers to communications operating via the Internet (Internet Protocol).
- It, in turn, is part of an expanded VoIP system; it is this technology that provides online viewing of movies, hosting webinars and much more.
- IP communication is implemented using a number of protocols such as SIP, Unistrim, MGCP, SIGTRAN, etc. SIP is considered the most famous and widespread; it provides session communication, that is, initiation, conduction and termination of a session in voice and video format.
The GSM gateway combines several formats at once; besides it, there are other bridges, but they are closer to professional ones, so people unknowingly associate them with GSM.
- CDMA equipment connects CDMA networks (radio communications) with urban analog ones.
- The UMTS bridge connects the city with UMTS networks. This is an improved version of cellular communication with 3G.
- GSM gateway for IP telephony is a narrow-profile equipment for transferring analogue communications to the Internet.
- Multigateway is a universal equipment that combines several formats at once, for example, GSM, UMTS and VoIP. It is these devices that are advertised and sold under the general name GSM gateway.
Device
In part, such a device can be called an analogue of a mobile phone, the operating principle is similar (via a SIM card), but the functions are different and the interface is designed differently, plus the software is special. The list of main differences includes the following:
- modern bridges can have from one to several dozen channels, with each channel having its own SIM card installed;
- presence of an analog FXO interface;
- presence of FXS voice port;
- the presence of digital options ISDN, BRI and PRI, which also provide connection to a mini-PBX.
One of the significant advantages is the ability to program each channel individually and automatically switch between channels as package minutes or traffic provided by a particular mobile operator are consumed.
Connection
Independently connecting a small device with 1 SIM card and several phones will not be difficult; the device has an intuitive interface, plus the documentation contains a detailed connection diagram. But you won’t be able to connect and configure multi-channel professional bridges yourself; this requires deep knowledge, so you can’t do it without a specialist.
Functions
The popularity of such equipment determines its rapid development; bridges are constantly being improved and supplemented with new functions, but there is still a certain list of services that all such devices can provide.
- Callback function – allows a cellular network subscriber to order a call that will be incoming for both parties (the call is made from a mobile phone to the device’s SIM card).
- Packet transmission of information via GPRS and EDGE.
- The device supports fax connection.
- Transmission of both single and group SMS messages.
- Connection and programming via computer.
- Multilink bridges have a router function that selects the most affordable connection option.
- Record telephone conversations in automatic and manual modes.
- Statistics and chronology of calls by time and duration.
Single-channel gsm gateway or GoIP VOIP Gateway GSM Converter SIP IP Phone Adapter
I present to your attention a miracle of Chinese technology called GoIP gateway. In short - it’s worth taking, it performs its functions with a bang. For those interested, please see the cat: What is it and what is it for, Vicki
VoIP gateway (Voice over IP gateway) is a device designed to connect telephone sets or office PBXs to an IP network for transmitting voice traffic through it. Device
VoIP gateways can have different capacities (number of telephone interfaces), differ in design (desktop version or in a 19″ rack) and power supply (built-in or external). A VoIP gateway usually has a built-in router that supports a wide range of routing protocols, user authorization with the ability to automatically obtain and distribute IP addresses (as a server and a client), set priorities for various types of traffic (QoS, Quality of Service) and have sufficient a set of functions for bandwidth management, network security, traffic accounting/analysis and administration.
The difference between a VoIP gateway and a PBX expansion card
the cost of VoIP gateways is several times lower (per channel); the costs of installing, configuring and maintaining VoIP gateways are noticeably lower (due to the fact that this work can be performed by our own IT service); increasing the number of VoIP gateway channels also costs several times less (expansion modules are purchased); VoIP gateways are better compatible with VoIP equipment from other manufacturers (the likelihood of problems when connecting with the equipment of an IP telephony operator is noticeably less).
Reduced costs for long-distance and international calls
How do you usually make a long-distance or international phone call from the office? An employee dials a number on his work phone, and the call goes to the office PBX. Through the PBX, the call goes to the local telephone operator (for example, MGTS), then through the zonal operator and long-distance/international communication operator (for example, Rostelecom or MTT) the call arrives in another city. And there, through another local communications operator, it reaches the desired subscriber. Due to the traditionally high tariffs of long-distance operators, companies with a large volume of long-distance/international traffic have always looked for ways to reduce costs. The solution was VoIP technology, which allows you to transfer voice traffic from traditional telephone networks to IP networks (Internet). At the same time, VoIP gateways began to be used to transfer traffic.
A VoIP gateway is connected to an office PBX and configured to work with one or more IP telephony operators. The cost of calls from IP telephony operators in Russia is 3-5 times cheaper than from long-distance operators. Calls to other countries are 10-30 times cheaper through IP telephony operators.
After connecting the VoIP gateway, call forwarding is configured on the office PBX according to the following rule: all calls from landline office phones starting with the number “8” (forwarding by prefix) are automatically forwarded to the VoIP gateway. The VoIP gateway, in turn, routes calls to recipients through IP telephony operators.
How it all began: It was necessary to resolve the issue of reducing the costs of negotiations between our company’s employees and mobile numbers. 2 SIM cards with unlimited calls to all mobile operators of the Republic of Kazakhstan were purchased in advance. There's only one small thing left to do - purchasing a GSM gateway. After several days of requests for GSM gateways from local suppliers, it was decided to save money by ordering this thing on ebay. Because I had no experience using this device; I selected 1 single-channel gateway for testing. The choice fell on GoIP gsm-gateway. I contacted the seller, informed him of my intention to purchase this product from him and inquired about the discount (which was indicated in the lot). Prod said that for the discount you need to buy at least 2 pieces. Because The device was needed urgently, we agreed on an additional 35 for express delivery via DHL. Clicked buy it now, then the product changed the invoice taking into account +35e for delivery. The next day it turned out that DHL does not deliver to my little godforsaken city and the seller already sent EMS at his additional expense, providing a track.
The lot was paid for on January 15, sent out on January 16, and arrived on January 28. The parcel took 13 days (Not the fastest EMS parcel). I couldn’t take a photo of the parcel, but it arrived undamaged. This miracle was packed in a box like this
(TV remote control is present in almost all photos for scale)
other photos
Contents: GoIP1 power supply (EU-plug) patch cord no instructions
The device has 5 indicators Power - power supply RUN - blinks frequently if there is no registration on the server and 1 time per second after the device is registered on the server LAN - blinks when transferring data over the network PC - blinks when connecting a computer (s) CHANNEL - blinks quickly green , if the SIM card is not registered with the mobile operator and once per second upon successful registration. It has outputs: Card - SIM card slot 12v - power supply LAN - local network PC - local network There is a reset button to reset to factory settings.
Externally, the device inspires confidence - the body is without any burrs, notches, inconsistencies, smell, etc.
The task was to connect a GSM gateway via H.323 through an AVAYA miniPBX. Connect power, lan, insert SIM card. A trunk was raised on Avaya, a route pattern was registered, etc., but the hardware did not want to connect. Smoking of both Russian and English manuals began. Forwarding to a specific mobile number worked almost immediately, but dialing a specific number did not (later the reason was found, but more on that later) Configuration via the web is possible through 2 ports: PC or LAN. By default, the LAN has DHCP (that is, it receives the network address automatically from the dhcp server) and PC (192.168.1.1 by default). I plugged it into the LAN and found the assigned IP address via MAC on the DHCP server (pasted on the back sticker) and accessed the device through it. The default password is admin/admin. We go in and see the status
Here you can see the assigned IP, MAC address, SIM card operator and signal level. Everything is visible in the photo, I won’t list everything. Go to the Configuration window
Here you can: *select a language (English is available - by default and Chinese) *Time zone (+8 by default) *Network Tones (meaning signals from a cellular operator). I chose both for Slovenia. You can specify it manually. RF and RK no *configure LAN and PC ports *IVR is responsible for voice guidance of the device.
I chose both for Slovenia. You can specify it manually. RF and RK no *configure LAN and PC ports *IVR is responsible for voice guidance of the device.
Next Call Settings
Since I needed H.323, I provide the settings for it. Well, the main thing here is an H.323 ID (corresponds to the IP trunk on the Avaya) and a Default Voice Gateway - the gateway through which we will talk (in my case, the IP Avaya). The Phone number and Display Name fields do not seem to be processed by my cellular operator.
Call Divert
Here you can forward the call to a specific mobile number (Forward to PSTN), or set the Dial Plan (which is what we need). In the Dial Plan, we indicate to bite off the prefix “1” previously inserted into the trunk on Avaya. ATTENTION!!! It doesn’t work without a prefix. You can specify authorization either by password, or by trust list, or both. I don't need it, I'll leave it blank. In general, these are all the settings of the TOOLS Menu:
Actually, all the menu names speak for themselves, and I think they do not require special attention.
From the Avaya side, an IP trunk with the prefix “1” was raised, everything started
The device also supports SIP.
In total, after all the manipulations we have: As soon as an employee dials a mobile number (for us it is 8700, 8701, 8705, 8707, etc.) the miniPBX routes this call to this gateway. The gateway, as I wrote above, has a SIM card with unlimited calls. If this gateway is already busy (someone is currently calling a mobile number), the miniPBX redirects the call through a regular city line. Ultimately, the company has a reduction in employee negotiation costs for mobile calls
I consider the experience successful and in the future the number of goip gateways will increase to 3-4 pieces in order to FULLY cover the need for mobile calls and ensure that calls to cellular operators do not go through the city line (because they are more expensive)
The device easily pays for itself in 1 month.
After all the settings and testing, the device moved to one of the server cabinets. There was only room in the back 
For purchase I recommend instructions in Russian According to tradition
with kote
Why do you need a GSM gateway?
In our country, such devices are purchased by large and medium-sized companies to save money on communication services. Most often, the goal is to provide a cheap connection between an office stationary device and the mobile phones of the company's employees or clients. But the list of options for using gateways is constantly growing.
- The equipment allows you to quickly connect a company branch to the internal network.
- Organization of conferences via multichannel communication.
- International communications at affordable rates.
- Backup connection.
- Locks are great for large moving objects, such as river cruise ships. It is worth installing a mini-PBX, and all the cabins of the ship will be provided with stable communication.
- All devices are equipped with a remote antenna with a powerful signal amplifier, which makes them indispensable far from civilization, where the signal strength leaves much to be desired.
Benefits of use
The massive increase in popularity of such devices is due to a number of significant advantages.
- According to statistics, connecting a bridge in a large and medium-sized company allows you to save up to 40% on communication fees.
- If you install several SIM cards with preferential rates on a multi-channel device and configure the router correctly, then costs can be reduced to almost zero.
- Calls between different mobile operators will be charged as domestic calls.
- A headache for large offices is personal calls from employees. By connecting the bridge, all connections can be tracked minute by minute, recorded and even saved information on a remote server on the Internet.
Disadvantages of using GSM gateways
In fact, the only disadvantage of the bridge is considered to be that it is not profitable to use with a small number of conversations. If a person makes only a few calls a day, then there is no point in spending money on a gateway for 6-8 thousand rubles; the device will pay for itself for a very long time.
VoIP-UMTS gateways
The essence of the operation of VoIP-UMTS gateways is completely identical. This type of device also provides signal conversion. The only difference is the presence of support for third generation networks or 3G, which makes them more universal. Switching between 2G and 3G networks is performed automatically depending on the availability of one or another type. The model line of this type also includes gateways that are suitable for companies and offices of various sizes. The telephony functions available when using a VoIP-UMTS gateway are no different from the telephone functions in GSM routers. For more comfortable use, the system provides technology for monitoring the balance status and alerting when the balance is low.
To summarize, it can be noted that VoIP-GSM and VoIP-UMTS gateways are well-proven solutions for providing modern high-quality communications with a set of all necessary functions. In the end, it is worth noting that at first glance, VoIP-UMTS routers are more effective in any conditions, but such a judgment is not objective, since if the office is located outside the coverage area of the 3G network, then purchasing a device that supports third generation networks is not advisable. It will also be ineffective to purchase a VoIP-GSM gateway for an office located within 3G access, because telephony based on this network standard implies a higher data transfer speed, which has a positive effect on the quality of communication.
Which GSM gateway to choose
It all depends on for what purpose and for what load the device is purchased. So, if you are planning to install it in a small office or country cottage without a mini-PBX, then it would be reasonable to take a bridge with one SIM card and several FXO ports for connecting stationary devices directly.
For mini-PBX and IP telephony with the ability to organize video conferencing, install faxes and other useful options, you need a multi-channel gateway with VOIP and GSM, where each channel has its own SIM card and the more connection points, the more powerful the device should be.
How to save money using a GSM gateway
As already mentioned, there are many options for operating the bridge, but the main savings are observed when using the simplest scheme. Suppose an office employee with a mini-PBX connected to a city line needs to call a companion on his mobile phone.
A call from an office PBX first arrives at a city exchange, is converted there and sent to the cellular operator, and from it to the subscriber; in this chain, the most expensive is the transition from landline to mobile. If a gateway is installed, then the “freeloader” in the form of the city station disappears. An office employee directly calls the recipient using the internal tariffs of the cellular operator.
In conclusion, I would like to note that disputes surrounding the legality of installing such equipment periodically arise; some operators even try to block the owners of gateways, but at the moment there are no laws prohibiting the use of bridges, which means it makes sense to install this convenient, and most importantly, useful device.
0 0 Votes
Article rating